Gold futures are one of the types of futures contracts, which are one of the most attractive investment and earnings instruments.
A futures contract for the purchase/sale of an asset is concluded on a specified (clearly defined) future date at the current market value. The underlying assets that are the subject of the contract in the process of concluding a contract can be bonds and shares, currency and goods (gold in this case). It is easier to understand the essence of futures using an example: for example, a farmer planted wheat and, while it is growing, in the spring he agrees to sell the crop in the fall at today’s price of 150 rubles. Forecasters give a forecast for a favorable summer and a large harvest, so there is an assumption that there will be a lot of wheat and its prices will fall greatly, but the farmer does not want to sell for 50 rubles.
Therefore, in the spring he agrees to fix the price for selling the goods in the fall. It turns out that the futures contract fixes a certain price and protects the interests of the seller. At the same time, the goods will be shipped much later than the date of conclusion of the contract, but within a clearly specified time frame.

If you study history, many American and European markets were based precisely on agreements between suppliers of goods and merchants. The first paper contracts appeared simultaneously with the advent of writing. Dated several centuries BC, cuneiform tablets from Mesopotamia can be considered the first prototype of futures.
Futures contracts are often used for investment. Gold futures (Gold) is a regular exchange transaction in which 2 parties take part - seller/buyer.
The main distinguishing feature of any futures is the lack of desire on the part of the buyer to become the real owner of the physical commodity. Futures trading is carried out without the actual delivery of goods, and earnings are made through fluctuations in contract prices.
Main benefits of futures trading:
- A large selection of instruments for trading on various financial exchanges, opportunities for portfolio diversification.
- High liquidity of futures, which makes it possible to use different strategies in your work.
- Lower commission level.
- Guarantee collateral – when purchasing a futures, a trading participant invests less money than in the purchase of a real commodity: from 2 to 10% of the price of the underlying asset.
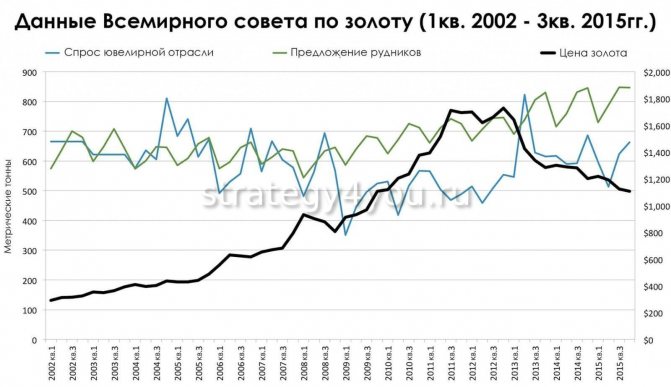
Forces of supply and demand
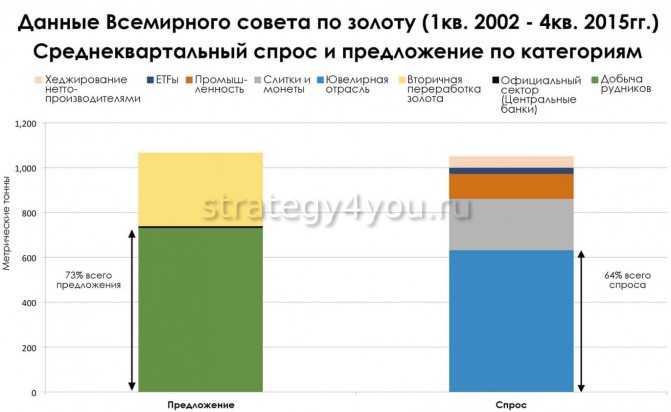
For more than a decade, most of the supply of gold comes from gold mines (about 73%), while demand comes from the jewelry industry (64%). Other factors and forces also influence the level of demand/supply: net producers, Central banks, exchange-traded investment funds. But their influence on the current situation in the market is more situational and changes significantly from year to year, which is noticeable even in quarters.
So, for example, in one quarter the demand for gold as a commodity by exchange-traded investment funds may be greater than the needs of the jewelry industry, while at another time the demand is approximately equal to the supply of gold mines.
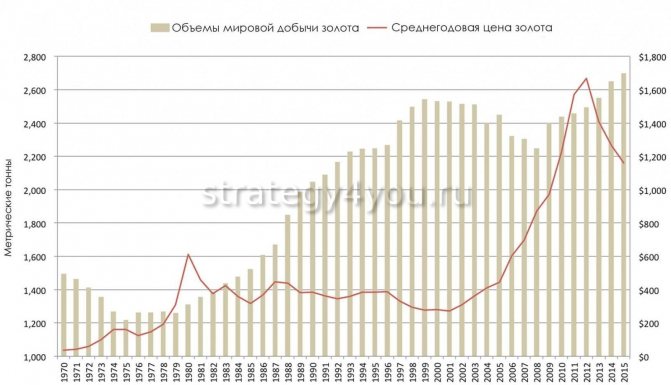
While the World Gold Council's physical supply/demand data is clear, jewelry demand and mine supply should directly correlate and influence the price of gold. But this usually doesn't happen.
On the graph you can see that the jewelry industry’s demand for gold decreased and increased, regardless of the supply of miners. Mine production volumes gradually increased, the cost of gold increased 6 times over the same period. Thus, it can be seen that the supply/demand forces of the jewelry industry and mines do not affect the medium/long term price of the metal.
But in a very long term, there is a correlation between the price of gold and its production due to the fact that it takes more than 10 years to put a gold mine into operation.
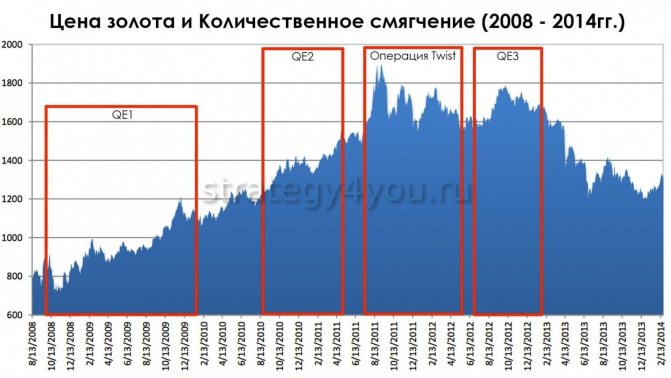
The price of gold in the medium/long term was influenced by the quantitative easing program (in English it sounds like quantitative easing, briefly QE) of the US Federal Reserve, which was launched after the economic crisis and was supposed to stimulate lending, reduce interest rates, and further repurchase from the asset market to the balance sheet Fed.
The program was implemented in stages: QE1, QE2 and QE3, carried out by the Federal Reserve of America from 2008 to 2014. The price of gold on the market significantly depends on the launch and success of the quantitative easing program and the passage of its subsequent stages. And it was in 2014, when the quantitative easing program in the country was curtailed, that gold fell sharply in price during the trading session after the news was released.
Gold Futures Contract Specifications
Gold futures can be purchased in the format of standardized, regulated exchange-traded contracts.
The main gold futures available to investors are:
- LME is the futures market of the London Metal Exchange, which is part of the New York Mercantile Exchange (COMEX) as a division.
- Tokyo Mercantile Exchange futures – TOCOM.
- Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
- Commodity exchange – Commodity Exchange (COMEX).
Volumes of metal futures, which are traded on the London and Chicago Mercantile Exchanges, as well as on the COMEX, are measured in troy ounces, prices are set in US dollars and cents based on one troy ounce of 995 gold. On the Tokyo Stock Exchange, futures are measured in kilograms and grams of 999 fines, and the price is determined in Japanese yen.
Trading is carried out during the current month; the next 2 calendar months; during any February, April, August, October (but within 23 months); any June, December (but within 72 months), counting from the current one. Contract trading stops 3 days before the start of the next calendar month.

One standard gold futures contract (ticker GC) has a volume of 100 troy ounces (equivalent to approximately 3.11 kilograms). Also used are E-mini Gold mini contracts (this is the ticker QO) with a volume of 50 ounces. The delivery micro contract is designated E-micro Gold (this is the ticker symbol MGC) with a volume of 10 ounces. All smaller than standard contracts are traded in the same months as the regular contract.
The price increment of a standard futures contract for gold on a futures exchange is US$0.10 or ¢10 (this is the tick representing the minimum change in value). When buying/selling a contract, profit/loss is determined by the number of ticks by which the price changes. To calculate the loss/income for each contract that is traded, first find out the cost of one tick.

Calculation of tick value for a contract:
- One standard futures contract has a tick size of 10 US dollars (100 troy ounces x 0.10). This means that each price movement by 1 tick will give a profit/loss of $10, with a change by 10 ticks – $100, etc.
- One mini contract – tick size 25 US dollars (100 ounces x 0.25). This means that each tick of the price will give a loss/profit of $25, if the price changes by 10 ticks - $250, etc.
- Micro contract – tick size 1 dollar (10 ounces x 0.10). That is, each price movement will give 1 dollar of profit/loss, and if the price changes by 10 ticks - 10 dollars.

The amount of funds needed to open a position intraday is the intraday (also known as intrasession) margin. The margin may be different, depending on the conditions of a particular broker, and may change. To trade a standard lot of gold (aka ticker GC) intraday, you need to have $1,000 and a certain amount for possible drawdowns.

Typically trade intraday (during the same trading session) and close positions before completion. When the position remains open until the next session, the transfer is carried out and initial and maintenance margin requirements are set. In this case, there should be more money in the trading account than in the case of intra-session margin.
Margin requirements for trading gold futures may change periodically in response to fluctuations in the value of the gold price to ensure adequate margins are maintained in participants' accounts.
As a rule, exchanges and brokers warn about changes in margin requirements at least 24 hours in advance: for example, in September 2021, requirements for CME Group gold futures contracts increased and in December 2021, the maintenance margin for a standard contract was equal to $4,450.
Kinds
Types of contracts by execution time:
- contracts for the current and two subsequent months;
- October (V), February (G), April (J) and August (Q) in an interval of 23 months;
- December (Z) and June (M) in an interval of 72 months.
Expiration occurs three days before the start of the next monthly contract.
Tickers:
- GS - Gold Futures;
- QO - E-mini Gold Futures;
- MGS - E-micro Gold Futures.
The futures contract identifier includes: ticker, trading month and year, for example GCJ9 - April 2021 contract.
How to use futures

Gold futures are considered a universal means of hedging transactions with precious metals. By selling futures, the seller insures against possible decreases in gold prices in the future. This provides a number of advantages, but also involves nuances. You can also trade gold futures on the Moscow Exchange.
Additional payments for gold futures:
- Exchange commission - so, the Moscow Exchange takes 1 Russian ruble from the seller when concluding a contract for 1 troy ounce, and 50 kopecks per trading day when opening/closing positions.
- The guarantee is always there, in this case it is equal to 6% of the contract value: the amount is blocked in the account until all obligations cease.
- Broker commission - its size is set in accordance with the tariffs, on average equal to the amount of the exchange fee.
To understand the essence of payments, you can consider an example. Thus, by selling 1000 contracts for refined gold per day (1000 troy ounces, the price of one is 1220 US dollars) with a contract expiration date of January 2015, the trader insures himself against a fall in price. To conclude a contract, the trader must make a contribution of 6% - this is 1220 x 1000 x 6% = 73,380 US dollars.

If the next day gold prices fall by $1 to $1,219 per ounce of gold, the trader will receive the difference as a result of the trading day (this is variation margin).
Types of futures contracts:
- Estimated – delivery of goods is not actually expected. Upon expiration of the contract, profits/losses are recalculated and funds are credited/debited.
- Deliverable – involves actual delivery of the underlying asset. The seller agrees with the buyer to conclude a deal for the supply of gold at the current price in six months, for example.
Futures is the current contract price. While this paper is in circulation, the value may change.
Here you need to distinguish between the price of the futures contract and the underlying asset. They are dependent, but these are different concepts. Thus, the futures price can rise and be lower/higher than the underlying asset, so it is formed according to circumstances.
Gold futures

Gold futures are an instrument of the exchange market, a futures contract for the purchase of gold, through which anyone can gain access to the precious metals market. Buying gold futures is one of the best ways to trade the precious metal at global prices and a popular way of investment.
The essence and parameters of gold futures
Gold is one of the most coveted commodities for most traders and investors. This metal has been mined for many centuries, and its popularity is due to its unique qualities, unique physical properties and small reserves. Most countries in the world use metal as the main means of making payments. At the same time, traders or investors buy gold to protect their capital and hedge against the instability of current exchange rates.
Gold is a valuable industrial raw material. Its features include corrosion resistance, good electrical conductivity, and unique chemical resistance. That is why the metal is very actively used in industry, including those associated with high technology.
Gold reserves are concentrated in various deposits throughout the planet. As a rule, the precious metal is found together with deposits of lead, quartz, copper, and in iron sulfite deposits. Large volumes of gold are dissolved in sea water, but they have not yet learned how to extract it. The main suppliers of the main precious metal on the world market are Russia, the USA, South Africa, the DPRK and a number of other countries.
During the period of the gold standard, major currencies were pegged to gold, but after the Great Depression (30s of the 20th century), many had to abandon such a system in the name of saving their economies. Since 1944 (after the conclusion of the Bretton Woods agreement), gold has again become part of the monetary system. At that time, the US dollar was recognized as the main currency, and all other monetary units were tied to it. This standard was in effect until 1971, when the convertibility of American currency into gold was abolished.
The price of gold largely depends on several factors - supply and demand for the precious metal. In addition, due to its active use as a gold and foreign exchange reserve, the price of the asset may change against the background of various economic and political events.
Today, a commodity such as gold is in great demand on a variety of exchanges, primarily in New York and London. At the same time, London trading is the leader in the total volume of purchased and sold gold. Since September 12, 1919, the London fixing has been the main reference point for market participants from all over the world. This is what is used in gold futures contracts. At the moment, the price of the precious metal is fixed between 10 am and 3 pm. These indicators are official and are used by central banks of various countries, traders and investors, refining and mining companies.
In terms of the volume of “paper transactions”, namely the conclusion of futures contracts for gold, one of the leaders is the New York Commodity Exchange - Nymex. There are other, no less important centers - in Sydney, Tokyo, Zurich and so on. The peculiarity of gold futures is that trading continues non-stop and lasts for 24 hours a day. As for the Russian Federation, gold trading here is in its infancy, and the trading system itself is still poorly developed (including at the legislative level).
Essentially, gold futures that trade on the COMEX (one of the divisions of the NYMEX) are a real commodity for traders and investors. The latter can buy assets at market prices. The advantages of such futures are their accessibility to everyone and the opportunity to profitably invest their funds. In this case, you can invest not only in bullion, but also in gold mining companies or coins. It is believed that there must be a place for the precious metal in an investment portfolio.
Gold futures are one of the most valuable and important instruments for commercial buyers of precious metals and gold mining enterprises. As a rule, gold futures are actively used to protect against price risks and increase the overall profitability of the portfolio. At the same time, specific strategies for purchasing gold futures contracts largely depend on the approaches of market participants themselves and the types of their activities.
The main parameters of gold futures include:
1. The underlying futures instrument is a refined precious metal (expressed in bullion). 2. One lot is one troy ounce of metal. 3. The value of the futures contract is indicated in one currency. As a rule, these are US dollars. The unit is the troy ounce. 4. Futures are usually settled on the day of execution. 5. On the Moscow Exchange, gold futures are executed in March, June, September and December. 6. The exact date of execution is the 15th of the month and year.

Gold futures: properties, strategies, pros and cons
The cost of gold at which purchase and sale transactions are carried out directly depends on exchange prices for the metal in the world (as already mentioned, accounting is carried out according to the London fixing). As soon as metal prices begin to rise, the holder of a gold futures contract can safely close the deal and make a profit.
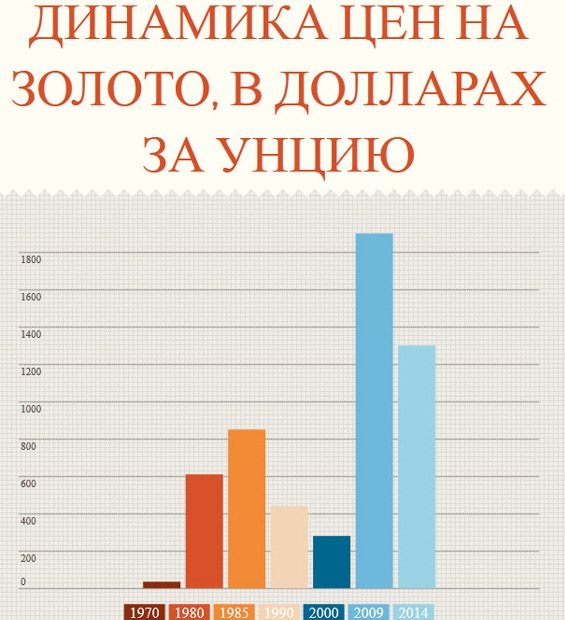
What factors determine the price of gold? As a rule, it depends on the economic situation, foreign policy of the largest countries, supply and demand, price dynamics on world currency markets. For example, changes in the value of the US dollar tend to be inversely proportional to movements in the price of gold.
Often gold futures are compared to OMS (non-personal gold accounts). But due to many disadvantages, the option with compulsory medical insurance is far from the best for most investors. For example, for unallocated metals, bank purchase and sale rates may differ by 3-5%. For this reason, the investor inevitably loses part of his capital. Another special feature of non-cash metal is that it can only be sold to a bank (even if there is a buyer willing to offer a higher price). Another disadvantage of impersonal gold is the impossibility of transferring it to another account (for example, when changing permanent residence). In such cases, it is necessary to close the current account and open it at a new address.
Transactions related to the purchase of gold futures are much more convenient and profitable. For example, when working with such tools, a market participant faces minimal overhead costs, which significantly reduces overall financial losses. As a result, profits can be obtained even with a slight increase in prices on the world market.
The main advantages of trading gold futures include:
— standardization of contracts, that is, most of the conditions have already been agreed upon by the exchange, which eliminates risks when making a transaction;
— the price of an asset does not depend on the condition of the metal itself, for example, the presence of a scratch or other damage on it. The main influence is exerted exclusively by market factors;
— when buying a futures, you can immediately sell it at the most favorable price for yourself. At the same time, there is no need to physically keep expensive metal with you;
— registration costs are minimal. In addition, there is no need to pay for renting a safe deposit box in a bank for storing gold bars;
— maximum liquidity. Gold is always in demand on the market, and you can make money even on minor price fluctuations;
— the ability to conduct round-the-clock trading;
— availability of free terminals.
But there are also disadvantages to trading gold futures:
— increased risks with increasing leverage;
— certain time restrictions that complicate working with the tool.
When working with gold futures, you can use several strategies, each of which has its own nuances. Thus, the most popular gold futures trading strategies include:
1. Hedging the risk of rising gold prices. If a trader plans to make a transaction to buy physical metal after some time, but is afraid that its price will rise, then he buys a gold futures contract today with the date he is interested in and the fixed price of the metal. This trade is called long hedging. The peculiarity of the strategy is that the buyer of gold futures insures himself against a possible decrease in the price of the asset after a certain period of time.
2. Hedging risks from a decrease in gold prices. If a trader plans to buy gold in the future, but is afraid of a decrease in its price, then he sells a gold futures contract for a certain period and at the desired (fixed) price. This type of transaction is called short hedging. In this case, the sale price of a physical asset is fixed, and the investor himself is insured against possible price fluctuations.
3. Short sale. Even in the absence of physical gold in circulation, a market participant can play to reduce the price. This is exactly what gold futures are used for.
4. Trading with leverage on the rise (fall) in the value of gold. In recent years, gold futures have become an increasingly attractive asset for trading for rising or falling prices. The leverage available to the trader (1:20) allows one to count on a very decent profit. In this case, the minimum amount of guarantee (collateral) when making a futures transaction is 5%.
5. Calendar spread. The essence of the strategy is making simultaneous transactions with several futures contracts. At the same time, the trader’s task is to play on the price difference between them.
Basics of gold trading on FORTS
FORTS is an abbreviation that stands for “Futures and Options of the Russian Trading System” (FORTS). In English, the decoding indicates the following meaning: “Futures&Options on RTS”, because FORTS appeared as a result of the merger of the St. Petersburg and RTS stock exchanges. It was with the emergence of this platform in 2001 that the Russian derivatives market began to actively develop.

Today, futures of the most liquid securities of the Moscow Exchange are traded on FORTS - these are shares of Sberbank, Gazprom, Rosneft, Norilsk Nickel, Lukoil, etc. Futures on indices and commodities are also traded. FORTS gold futures offer the largest selection of instruments for making transactions for the sale/purchase of precious metals in the country.
The main advantages of using FORTS:
- A good opportunity for beginners who have small amounts of funds (here you can start trading with 15,000-30,000 rubles).
- Gold can be easily and quickly converted into money.
- You can work at any time of the day, and late too (when Western stock exchanges are operating).
- Thanks to the low guarantee, a trader can manage capital that is many times greater than his own, earning an appropriate profit.
Gold futures are an interesting and definitely worth attention instrument that can be successfully used for investing and making money, provided that you study the features of trading and the algorithm for making transactions.
Futures history

I would like to start this article with the history of futures itself, and it begins in North America from the mid-19th century and operates in all major countries until the present day. For a full year since the market opened, futures have been trading in agricultural commodities and precious metals. Towards the end of the 20th century, trading in securities and oil took place. Now there is active trading in gold and other precious metals.
What are futures contracts for precious metals and what are they used for?
A futures contract allows anyone to start trading precious metals such as platinum, palladium, gold and silver. This is currently the best way to make money from precious metals. This is much more convenient and accessible than conventional investments in bullion, money, shares, etc.