I welcome guests who are interested in the yellow precious metal and everything connected with it! This article will focus on unrefined gold, which has not yet been processed after mining. As you know, gold, according to the periodic table, has the lowest activity, so its main part is found in the ground in the form of pure nuggets or with elements of ingrained rock.
Today I will pay attention to such a phenomenon as spot gold. We will find out its features, methods of mining and cleaning it from debris, and also analyze the value of this raw precious metal.
Content
- 1. What does the word “Shlikh” mean?
- 2. How to purify schlich gold
- 3. What is the schlich search method?
For many generations, a metal such as gold has been highly valued for its properties: ease of melting, elasticity, extraordinary shine, and it does not oxidize. This is one of the first precious metals known to mankind, because searching for it does not require much effort or special equipment.
Depending on where the gold is located, you can extract a type such as schlich gold. It is not yet purified, not melted, in the form of small grains or larger particles in the ore.
How to choose gold leaf for gilding
The choice of material for gilding is a very important point, because using low-quality material, you will get an unimportant result after spending much more time. In addition, it is hardly worth saving on gold leaf. Some gold producers or sellers try to sell bad and low-carat gold at the usual price for good gold. You should be careful and buy from a trusted manufacturer. Bad gold is holey, low-karat gold with defects such as moire, which is poorly polished and oxidizes. It’s easy to calculate that using holey gold in 2 layers (and it’s impossible even for the most experienced gilder to gild one layer of holey gold) you’ll overpay for the book at least 2 times! How much extra effort will it take? Is this saving worth it, as well as the ruined mood? You can save on tools and workshop equipment, but we consider it uneconomical to save on materials =)
We use gold from the Russian company Raritet, whose production is located in Belgorod and which has never let us down in terms of gold quality. Their website is susalnoe.ru. We are not their representatives/agents and this is not a paid advertisement , we just found good quality gold at a good price and recommend it to you too. However, you can use the gold that you are used to and trust, but good gold, in our opinion, must meet the criteria below.
gold Raritet, branded packaging
Gold should ideally be 23.5 carats , a reduction to 20 for yellow and red and up to 17 carats for color is allowed (color is achieved through the use of various alloys, so the carat is logically reduced). Gold below 14 karat will already be highly oxidized. It's also not worth taking 24 carats . Although it is almost 99.9% pure gold, it turns out to be somewhat fragile, not elastic, and during transportation or application it can break and tear more easily than 23.5 carat gold, where silver and copper are added for ductility.
Also, for polymer gilding, you should only take free gold , not transfer gold! Transfer gold is hammered into tracing paper and is suitable for use only in gilding on the face. In our gilding of free gold, we make a “pseudo-transfer”, which is ideal for gilding flat surfaces, such as icon boards. You can read a little more about this pre-revolutionary method of gilding without using a lampemsel in this article about the mistakes of beginning gilders, and you can learn how to gild this way at our master classes (you can read the program and sign up here).
Gold must be clean, without moire or streaks. Moire looks like glass on a frosty morning in the village - beautiful stains or “marbling” (by the way, in interior gilding this defect is not always considered such; some people like such imperfect gold, but this is not suitable for icons). This defect results from the lack of gold production at the plant, often with fully automated gold production.
Also, gold should not be too shiny right away on the book. This effect is a consequence of the low carat gold, where there are large inclusions of tin. This is often the case with Chinese manufacturers and dishonest sellers who pack cheap Chinese analogues into high-quality gold books.
How to recognize a fake?
- It is advisable that the book be sealed (for example, Raritet generally seals some books with sealing wax)
- Gold shouldn't sparkle too much already in a book
- Some bring gold that was sold to them as “German”, but there is a picture glued to a simple paper book, blurred on a black and white printer, with the logo of a good German gold production company, Eyzinger. Do you think the Germans will begin to pack their gold in such books? For comparison, you can look on the Internet to see what a book from a truly German manufacturer Noris looks like - it is colored, with a branded label and a hologram.

Noris gold, branded packaging
4. A fake is most often very poorly polished and oxidizes already in the book.
Our advice is to find a good supplier of gold, no matter what company it is, and do not try to save 500 rubles on an unknown book by then putting gold in 2 layers or using it on a piece of gold (by the way, you can read about how to make melted gold for gold-white writing in this article). Although in fairness, it is worth noting that some guys bring really good quality gold from Europe, which is not too expensive. Unfortunately, according to our experience and the experience of other gilders from around the world, gold from European producers sold in the EU and other markets is often of different quality, even being packaged in an official book with all the required logos. What is the reason for this? Unanswered question at the moment.
Thickness of gold.
For icon boards, we recommend using gold with a ligature weight (what is a ligature weight? You can read in this article) 1.25 or 1.4. The maximum thickness for seamless gold plating is 1.6. But this is already very thick gold, which is simply not rational to take. Gold 2.0 and above is used for exterior work only and will almost always leave seams. Beginner gilders like to buy thicker gold, as they are afraid of tearing very thin gold. However, gold 1.25 and gold 2.0 tear about the same, but thick gold almost always gives joints. Well, gold 2.0 costs almost 2 times more.
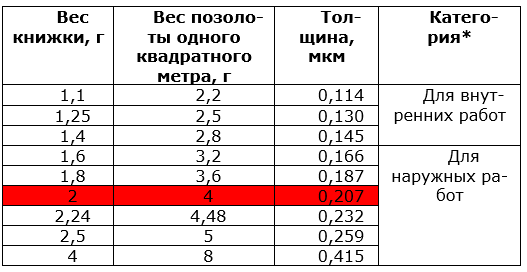
recommendations from the site susalnoe.ru
Is it possible to use gold leaf for gilding an icon? We decided to discuss this topic in detail in a separate article.
In our lessons we teach how to gild in one layer with fairly thin gold, 1.25, which will save you a lot of time and money. (You can read about how to sign up for our classes here).
We allow you to copy the materials of this article on any resource, but we ask you to always keep an indication of the original source of publication - //agat-zub.ru/stati-po-zolocheniyu/kak-vybrat-susalnoe-zoloto-dlya-zolocheniya
What does the word “Schlich” mean?
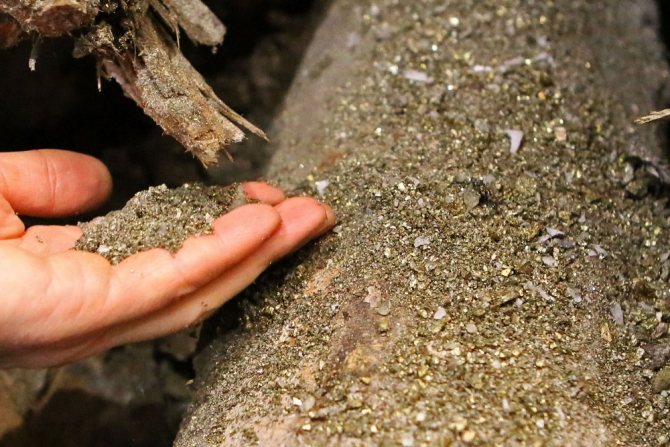
The word “concentrate” means a concentrate of heavy metals and minerals extracted from natural sediments or rocks, which remain in the water after washing due to their dense structure. This term also includes small nuggets.
This type of gold is one of the cheapest, since the metal has not yet been processed and contains a significant amount of various impurities - silver, copper, iron. The main fossil is approximately 80-90 percent, sometimes the figure reaches 97% (it is much more expensive). The highest standard is the number 999 - this is an indicator in which only 0.1 is an admixture of other metals.
Device for extracting gold from fine concentrates
The utility model relates to the gold mining industry, in particular, for the extraction of gold from finely dispersed concentrates containing mainly magnetite and finely dispersed gold and can be used in processing factories and concentration plants. The utility model consists of a device for extracting gold from finely dispersed concentrates, having continuous loading and unloading, consisting of a chamber for separating magnetite with additional magnets, made in the form of a vertical container made of non-magnetic material, a chamber for collecting the gold-containing non-magnetic fraction, rotary valves with hinges , having open and closed positions, a special device-divider for forming a series of flows from the loaded concentrate, while the extraction of gold occurs in the non-magnetic fraction during the free fall of particles in an aqueous environment. 1 s.p. formulas; 1 ill.
The utility model relates to the gold mining industry, in particular, for the extraction of gold from finely dispersed concentrates containing mainly magnetite and finely dispersed gold and can be used in processing factories and concentration plants.
There is a known gateway for the enrichment of placers and concentrates with rubber mats, on the front compartment of which there is a rotating magnetic drum with a scraper for removing magnetic minerals from the enriched material [1]. The disadvantage of this invention is the inevitable drift of gold into tailings (magnetic fraction). This is due to the fact that the field lines of permanent magnets, self-fixed on a metal drum with alternating poles, are closed between opposite poles, especially at the junctions of the magnets, and strands of magnetic minerals lined up along the force lines pinching minerals, including gold particles, are carried away into the tails. thereby reducing the efficiency of extracting the useful component.
The closest to the proposed utility model is a device for removing magnetite during the enrichment of finely dispersed concentrates [2]. A device with continuous loading and unloading includes a chamber for separating magnetic minerals in the form of a vertical container having a rectangular cross-section of 200×100 mm and a height of 180 mm made of non-magnetic material, equipped with fixed permanent magnets on the outside, as well as a chamber for collecting the non-magnetic fraction with a rectangular cross-section of 200 ×40 mm with a height of 70 mm and a divider device. The disadvantage of this device is the insufficient efficiency of extracting the useful component, caused by the inevitable drift of gold particles into the separation chamber
magnetite. This is due to the fact that magnetite particles, when free falling in
magnetic field, moving horizontally to the poles of the magnets, they hit gold particles, changing their trajectory from a vertical fall, thereby reducing the extraction of gold into the non-magnetic fraction by carrying them into the magnetic fraction.
The essence of the utility model is that in the proposed device, which includes a chamber for separating magnetite, made in the form of a vertical container made of non-magnetic material, having a rectangular cross-section of 200×100 mm and a height of 180 mm, equipped with fixed permanent magnets on the outside, a chamber for collecting the non-magnetic fraction with a rectangular cross-section of 200×40 mm and a height of 70 mm, a dividing device for forming a series of flows from the loaded concentrate, characterized in that the chamber for separating magnetite is equipped with additional magnets, while rotary valves are installed in the lower part of the permanent magnets to separate magnetic and non-magnetic fractions, the divider is made in the form of a sieve, with a size of 200×40 mm and has cells of 2×2 mm.
The use of such a device in the practice of mineral processing, for example, for the extraction of gold from fine concentrates, is unknown. Thus, the claimed utility model meets the “novelty” criterion.
In comparison with known technical solutions, the proposed device has new properties:
— the use of rotary valves with hinges in the open position, installed below permanent magnets, allows for increased gold recovery due to additional cleaning of the chamber on additional magnets to isolate magnetite;
— the use of butterfly valves in the closed position prevents magnetite particles from entering the non-magnetic fraction, which improves the quality of the gold-bearing non-magnetic concentrate.
Thus, the proposed utility model meets the “inventive step” criterion.
A device for extracting gold from finely dispersed concentrates is shown in (Fig. 1) and consists of a loading hopper 1; dispenser 2; loading funnel 3; divider 4; pipe 5; chambers for separating magnetite 6; overflow tank 7; magnet retraction mechanism 10; permanent magnets 8-9; additional permanent magnets 12-13; rotary valves with hinges 11, having open (A) and closed (B) positions; chambers for collecting non-magnetic fraction 14; valves for water release 15 and 16; hatch for unloading magnetic fraction 17; hatch for unloading non-magnetic fraction 18; collection of magnetite 19; collection of gold-containing non-magnetic fraction 20. All components of the device (except magnets) are made of non-magnetic material, for example stainless steel or duralumin.
The chamber for separating magnetite 6 is made in the form of a vertical container, rectangular in cross-section (200×100 mm) and 180 mm in height. The bottom of chambers 6 and 14 have an inclination angle of 50-60°, the continuation of which is a magnetite collection 19 and a collection of gold-containing non-magnetic fraction 20, in the lower corners of which there are hatches 17, 18 for unloading fractions. In the lower part of the chamber for separating magnetite 6 there is a chamber for collecting the non-magnetic fraction 14, which is also made of non-magnetic material. Chamber 14 has a rectangular cross-section of 200×40 mm and a height of 70 mm. Rotary shutters in the open position (A) have an inclination angle of 60° and are designed to direct the gold-containing non-magnetic fraction into chamber 14, and when closed (B) they prevent magnetite from entering the chamber to capture the non-magnetic fraction during its removal for a short period (1-2 sec) removing magnets from the walls of chamber 6.
The concentrate is fed from hopper 1 by dispenser 2, from which the concentrate enters the loading funnel 3 and onto the divider 4, which is a sieve with a size of 200×40 mm, with a mesh of 2×2 mm,
which, from the total mass supplied to the loading of concentrate, forms about 500 flows, as a result of which the demagnetization and productivity of the installation are significantly increased. A continuation of funnel 3 is pipe 5 of rectangular section 200×40 mm. The lower end of pipe 5 is 50-70 mm below the water level in chamber 6. The productivity of the device is 50-60 tons/year.
The described device for extracting gold from finely dispersed concentrates was tested on a laboratory installation similar to that described above, i.e. which is its model analogue. The most typical size class of finely dispersed concentrates, 0 - 0.315 mm, was subjected to enrichment. Brass serves as an imitation of the useful component (gold).
An example of a specific comparison of the efficiency of enrichment of a useful component on the proposed (two-section) device with a prototype, performed in laboratory conditions using the well-known Hancock-Luyken formula, %, is given in Table 2; ref—content of simulants in the original ore, 9 g/t; k - average concentrate yield, %; (k) — average content of simulant in concentrate, g/t.
| Table 1 | ||||||
| Comparison of the enrichment efficiency of the prototype and the proposed device | ||||||
| experience | Devices | |||||
| Prototype | Proposed | Prototype | Proposed | |||
| Simulator extraction, and, % | Simulator extraction, and, % | To | To | To | To | |
| 1 | 60 | 71 | 20 | 29 | 13,7 | 44 |
| 2 | 57 | 69 | ||||
| 3 | 61 | 67 | ||||
| Average value | 59 | 69 | ||||
| Efficiency of enrichment of useful component (), % | 42,8 | 60,76 | ||||
As can be seen from Table 1, the efficiency of enrichment of the useful component on the proposed device is 1.41 times higher than that of the prototype, which can be considered very effective.
Information sources
1. Utility model of the Russian Federation 6348 U1 6 VOZV 5/70 / Gateway for the enrichment of placers and concentrates / Larionov V.R., Fedoseev S.M., Vinokurov V.P., Matveev A.I. BI 4 04/16/1998
2. RF patent MKI B03C 1/02 2149701 / Device for removing magnetite during the enrichment of finely dispersed concentrates / Novopashin M.D. et al. publ. BI 15 05/27/2000. Application 12/25/1997
A device for extracting gold from finely dispersed concentrates, including a chamber for separating magnetite, made in the form of a vertical container made of non-magnetic material, having a rectangular cross-section of 200×100 mm and a height of 180 mm, equipped with fixed permanent magnets on the outside, a chamber for collecting the non-magnetic fraction with a rectangular cross-section of 200 ×40 mm and 70 mm high, a divider for forming a series of flows from the loaded concentrate, characterized in that the chamber for separating magnetite is equipped with additional magnets, while rotary valves are installed in the lower part of the permanent magnets to separate the magnetic and non-magnetic fractions, the divider is made in the form sieves with a size of 200x40 mm and have cells of 2x2 mm.
How to purify schlich gold
This procedure is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming; it is called refining or refining.
There are three ways of such processing:
- • Electrolytic . This is an electrolysis process in which gold with impurities is the anode, and a plate of pure gold serves as the cathode. In the process, the pure precious metal is separated from impurities and accumulated on the plate.
- • Wet method . Is the easiest way. Gold with impurities is placed in concentrated sulfuric acid, with this action all impurities are dissolved, and the metal is subsequently extracted and melted.
- • Dry refining, chlorine treatment . Chlorine gas is passed through the impurity to separate the precious metal. The simplest and least labor-intensive method.
Search method - reconnaissance, documents, washing.
To find a gold mine in our time, you will have to work hard; in the 21st century, all possible locations of gold have been studied and processed. And yet, the Ural region, the so-called “golden belt,” stores in its depths a considerable amount of precious metal. In our Sverdlovsk region, according to State Reserve documents, 232 deposits are registered with total reserves of categories A+B+C1 = 162,000 kg, C-2 = 128,000, and off-balance reserves 54,000 kg. The search method involves carrying out certain work.
Gold miners have to search for deposits in stages:
- study the geological structure of the deposit to take samples of loose sediments;
- draw up documents for production development;
- clear the area of top layer rocks;
- wash the concentrate sample with current documentation;
- wash control samples to determine the area of deposits;

Each stage of gold mining requires certain information, technologies and tools. From official historical sources it can be reliably stated that the first Russian mine began operating in 1747 in the city of Berezovsky. The impetus for the development of gold mining was a nugget found by Erofei Markov, a resident of the village of Shartash, the first mine was named Initial, followed by Listvennichny, Komarovsky, and Nebogaty. In 1754, the first gold mining plant was built in the city of Berezovsky and more than 50 mines were opened, producing large quantities of pure gold.
- Since 1805, more than 140 gold-bearing veins have been found in the mines and several dozen mining mines have come into operation. In the Urals, in the Sverdlovsk, Chelyabinsk and Tyumen regions, more than 70% of the mines operating at one time were located, and today about 20 tons are extracted from the subsoil of the Ural soil. Our Sverdlovsk region accounts for 11 tons of the total production.
The second point of work after determining the location of the search for gold metal is the preparation of permits and clearing of the soil from the rocks of the upper layer. Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs can engage in the development of gold deposits. The license for production is issued by the Federal body ROSNEDRA, which has offices in different regions of Russia; in the Sverdlovsk region, all issues related to minerals are resolved by the Ural Agency for Subsoil Use. Legal organizations receive licenses for a period of 20 years or more, private entrepreneurs can develop deposits without industrial volumes for a period of 5 years.
- Starting from 2021, private entrepreneurs have been introduced with additional rules that are mandatory. Mining is permitted by the surface method using hand tools, blasting, tractors and other equipment are prohibited, the mining depth is not less than 5 meters, people strictly specified in the contract can participate.
Site clearing is a process that has technological features, because it is advisable to carry it out at certain times of the year to reduce labor costs and the tools needed for work. The most suitable time of year for such work is the end of winter, when bushes and dead wood easily break down and the top layer of soil in peat areas is separated without complications. With a work plan thought out to the smallest detail, at the beginning of spring you can calmly begin working on the so-called balance sands and begin slurry washing.
Manual washing of rock is a responsible and labor-intensive task that requires certain skills and high-quality tools. Good work will make it possible to accurately determine the presence of gold metal and identify places with the highest concentration. Washing is carried out using wooden trays made of hardwood of various designs; the professional names of the trays are Oriental, Siberian, Korean.
The peculiarities of the options for obtaining heavy minerals make it possible to extract large grains from placers, mainly in the form of nuggets.
Finishing of sluice concentrates with fine gold without loss.
When extracting gold from alluvial deposits, industrial washing devices are widely used, using sluice and other technologies to isolate rough gold-containing concentrate, which is sent for further enrichment (finishing) in order to increase the gold content to 20% and higher, up to the separation of schlich gold, suitable for melting into an ingot.
At the head of finishing operations, traditional processing equipment is used: jigs, concentration tables, screw separators and sluices, centrifugal concentrators, magnetic separators.
There are often cases when manual finishing on trays, blowing, and acid etching are used, which significantly worsens the working conditions of workers involved in processing and the environmental situation. In addition, these processes entail inevitable losses of gold.
To solve problems associated with finishing, it offers a beneficiation complex for finishing gold-containing concentrates. The finishing complex was created at the request of miners to minimize gold losses.
We present to your attention the ITOMAK beneficiation complex for finishing gold-containing concentrates . The finishing complex was created at the request of miners to minimize losses during finishing. To solve these problems, unique equipment has been specially developed.

It uses the following equipment:
- SMS-20, dry magnetic separator with a capacity of 20 kilograms of dry material per hour. The maximum intensity of the magnetic field created by the device in the separation area reaches 2 Tesla.
- Centrifugal concentrator Itomak KN-1, a small-sized, highly efficient concentrator that allows you to additionally extract almost all fine gold from the tailings of the concentration table.
- SMZh-PM-3, magnetic fluid separator, a small-sized, highly efficient separator that allows you to separate concentrate gold from non-magnetic, heavy impurities (allows you to eliminate concentrate stripping and speed up the finishing process). The separation principle is based on the ability of magnetic fluids to change their density in a magnetic field.
Main advantages of the complex:
- it is possible to supply source material with a particle size of up to 70 mm;
- separate enrichment of class -2 (3) mm and +2 (3) mm, due to the installation of a jigging machine at the head of the process;
- the presence of a control operation of gravitational enrichment of the “tails” of the concentration table (will allow you to catch lamellar, dusty, porous gold, as well as intergrowths of gold with the rock);
- includes a full cycle of wet and subsequent dry finishing to obtain spot gold for further smelting;
- easy to set up and does not require constant process adjustment (when working on the same material);
- the complex located in containers is highly mobile and can move along with the washing device as the placer is mined;
- universal, suitable for processing concentrates from all existing sluices, concentrates from jigs and centrifugal concentrators, slurry tailings (SHOU, SHOF), it is also possible to process the ephelium fraction of washing devices (with a capacity of up to 2m3/hour) in order to determine real losses or obtain additional metal .
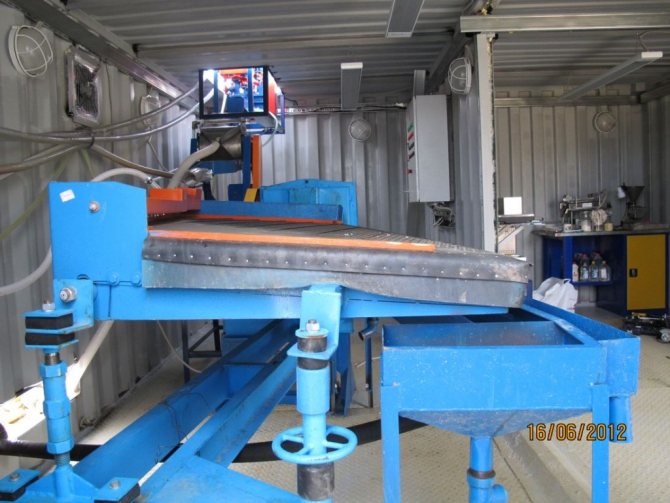

Finishing module
The proposal for the supply of the finishing complex includes:
- development of a technological scheme for finishing processing and selection of main equipment, taking into account the initial data provided by the Customer on the raw materials planned for processing;
- specification and preliminary cost for complete and partial installation of the necessary basic equipment, as well as the cost of the turnkey complex.

Rice. 1. Schematic flow diagram of the finishing cycle.
All equipment is equipped with consumables, spare parts and technical documentation and is ready for installation and start of work.

Over the past 2011 and 2012, these complexes were supplied to the following organizations:
- Artel of prospectors "NORTH" - 2 complexes;
- Artel of prospectors "Golden Pole" - 2 complexes;
- Artel of prospectors "OINA" - 1 complex;
- Mine "Udereisky" - 1 complex;
- LLC "Kolyma Prospector" - 1 complex;
- CJSC "Kamensky Quarry" - 1 complex;
- LLC "Gazimur" - 1 complex;
- Khan Tengri Goldberg LLP, Republic of Kazakhstan – 1 complex;
- Troika Investment Group LLP Republic of Kazakhstan – 1 complex;
- "Geo Professional Services" LTD, Republic of Ghana - 1 complex.
There were only positive reviews from all enterprises.
So, for example: “Golden Pole” in the areas in the Mezhdurechensk region carried out the finishing of the concentrates of three locks on this complex, which was installed at the end of June 2012. During three months of work, an additional 33 kg of gold was recovered!!!
Over many years of operation, Itomak has proven its economic efficiency and technical reliability.
It can be used for mining natural and man-made deposits and allows you to extract up to 98% of free gold from the original rock with low operating costs.
S.I. Afanasenko - General Director of CJSC Itomak
Published in the magazine “Gold and Technology” No. 2(20)/June 2013