Of course, all pawnshops operate on the principle of issuing a certain amount of money for pledged property. In fact, the pawned item is stored in the pawnshop for a certain time, the client receives money to overcome temporary financial difficulties, and upon expiration of the agreed storage period, the client either buys his item back, paying certain interest and part of the money received, or abandons his property in favor of the pawnshop.
As a rule, the work of all pawnshops in Russia is structured in such a way that even after the expiration of the main storage period of the pawned item, there is a certain buffer zone - or a period with an increased interest rate. If during the additional period the client does not appear to redeem his property, then in this case it irrevocably becomes the property of the pawnshop and is then sold entirely at the discretion of the organization itself.
About the functions of a bill of exchange
A bill of exchange is a classic settlement instrument; perhaps no one should be convinced of this? In this case, a bill of exchange can replace cash. After all, it separates 2 acts:
- Payment.
- Receiving funds.
In fact, a bill of exchange should be perceived as one of the universal means of payment. Technically, the circulation of bills speeds up settlements and reduces the need for regular cash. Of course, in the context of developed commercial turnover. The thing is that by the time of payment, the bill can pass through a huge number of hands. And thus a whole chain of bill holders will pay off their obligations among themselves.
This is why vectors are used so widely in the field of international settlements. We are naturally talking about the processes of export and import. Another function of a bill can be considered a mechanism for storing funds. After all, like any security, with the help of a bill of exchange you can:
- Save your own money.
- Increase the nominal amount of money.
The scheme for making money on bills is not much different from the same activity, but with shares. You earn income on the difference between:
- Purchase amount.
- Sales amount.
The moment of sale of the bill is called redemption. As we said above, a bill can be considered as a form of lending. For the reason that it is with the help of this security that you will be able to process credit transactions of various types. Namely:
- Providing a loan to your borrower.
- Return of funds received (on credit).
- Receiving delays when receiving goods, etc.
In fact, the bill allows you to lend to borrowers without intermediary. But don’t rush to run for bills. This is not as simple a tool as it might seem.
Well, another key function of a bill is its value on the securities market. After all, bills circulate as securities on the market. Therefore, they can be bought and resold. True, this is not for small speculators. You need to trade bills very carefully, and they usually do not bring income in the short term.
What can you take to a pawn shop?
You can get a loan from pawn shops by handing over items of consumer value. Thus, the list of the most common collateral items includes:
- jewelry;
- household appliances and electronics;
- fur;
- antiques;
- construction and repair power tools;
- Sports Equipment;
- equipment for active recreation.
Of course, each individual company sets its own rules for accepting values. Today on the market there are highly specialized pawnshops that accept only one type of item (for example, only items made of precious metals or fur), but most are a universal type of organization. The list of accepted values is dictated not only by internal regulations, but also by the current legislation of the country and region.
Basic characteristics of a bill as a separate security
There won't be many features. This security is always transferred through endorsements. This is called an endorsement. The endorsement does not require certification by a notary. And only cash can be considered as the subject of an obligation under a bill of exchange. Separate characteristics for securities, which are called bills of exchange, include:
- Joint and several liability.
- Strict documentary form.
Let's start with joint and several liability. In fact, liability for the obligations imposed by the bill will be the most complete. If payment has not been made, the holder may sue. And not only for the primary drawer, but for all obligated persons. Even the order of endorsement will not be fully taken into account here.
And such a security is a full-fledged document, with a predetermined list of details. In fact, this limits the capabilities of the “issuer”. True, there is still no issuer, as such, for bills of exchange, because this is a credit security. But we hope the point is clear. All details of this document are initially determined by special Regulations. In our case, this is the Regulation on promissory notes and bills of exchange.
It is enough that one of the details is missing. That’s it, the security will no longer be considered as such. And all the details that were on the list of optional ones will not be taken into account here. Consequently, there are no arbitrary forms for the bill. It either complies with the Regulations or it does not. If it does not correspond, then such a bill cannot be considered valid.
It is also worth remembering that the security itself implies the presence of unconditional obligations. In other words, payments should not be tied to any external conditions. Even if something very serious happened, issuing a bill imposes direct obligations. If the obligations were not fulfilled on time and in the manner determined in advance, then immediate sanctions will follow.
At the same time, the bill is an obligation of an abstract nature. It is this feature that allows these securities to be exchanged and transferred without any restrictions or problems. If we are, of course, talking about the traditional security transfer scheme.
What is the essence of a loan from a pawnshop?
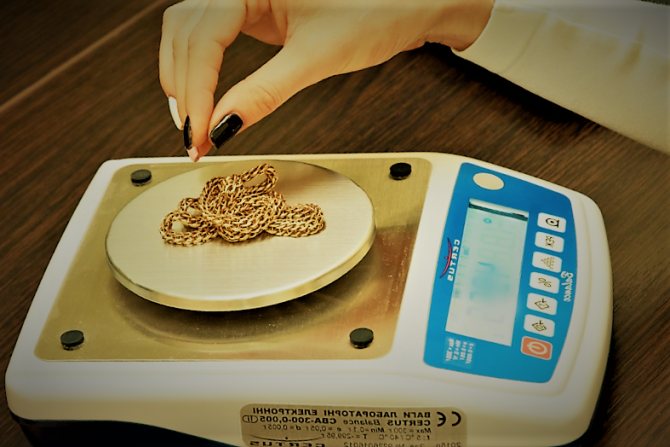
A pawnshop is a financial institution that issues money secured by property. Therefore, it is advisable to apply for a loan only to those who have something to pledge. It cannot be said that pawnshops offer more favorable conditions than banks. Now their services are quite expensive. Typically, people who don’t want to spend a lot of time applying for a loan from a bank turn to pawnshops for help. After all, it really takes several days. At a pawnshop, you can get money immediately after signing a loan agreement. Also, frequent visitors to pawn shops are clients who are not given loans anywhere else. This financial institution will not refuse, because it is not interested in how much a person earns or whether he works at all. The main thing is the subject of collateral.
General classification of bills
Let’s immediately decide that we will not consider bronze and friendly ones. In the first case, it is assumed to benefit from non-existent securities. In the second case, a scheme is assumed in which one solvent enterprise provides another with a kind of assistance. We are talking about transferring payment through a bill of exchange in favor of an enterprise that finds itself in a difficult financial situation. So, there are no bills of exchange on the territory of the Russian Federation:
- Bronze.
- Friendly.
The reason for this is very simple. The fact is that if such securities are in commercial circulation in large quantities, then inflation will begin. Not general inflation, but quite bill inflation. The thing is that obligations on such securities are usually not fulfilled on time. Which leads to aggravation of the situation. Moreover, non-cash securities allocate part of the resources (financial). And if funds are used in an unproductive manner, then they also depreciate. In fact, this became clear almost immediately. Therefore, such bills cannot be used on the territory of the Russian Federation. Because this was regulated by a separate letter from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation back in 1991.
In addition, according to Russian legislative norms, such securities are classified very conditionally:
- Translated.
- Simple.
Let's start with translations. They are also called draft bills. This is a full-fledged document that contains an unconditional order. This order is addressed from the drawer to the payer. The very content of the order is that a certain amount of money must be paid:
- In a specific place.
- Within the originally established time frame.
In fact, a bill of exchange involves the participation of three parties at once:
- Holder (payee).
- Debtor.
- Drawer of the bill.
It turns out that bills of exchange regulate trilateral relations at once. The debtor, based on the regulations, will become the main payer. Despite the fact that the drawer is also responsible, both for payments and for the acceptance of the bill itself. There are also solo bills. This is a simple security containing a standard requirement to fulfill obligations. And of course, these obligations must be fulfilled within the specified period. It must be understood that the obligation is:
- There was nothing to back it up.
- There was no condition.
But the obligation is binding. Because it is confirmed by a bill of exchange. If the bill is invalid or forged, then the obligation is lost. In addition, bills can be classified in other ways. For example:
- Rekta.
- Security.
- Blank.
- Financial.
- Commodity (aka commercial).
- Avalized.
Rekta bills contradict their original form. After all, they are issued in a specific name. Because of this, such a security cannot be transferred in favor of third parties. Because the security is registered.
Security papers are needed to secure a loan or loan. We are talking about lending to an unreliable borrower. And it is known in advance that it has reliability problems. Traditionally, such papers may be kept in debtors' escrow accounts. And they did not provide for the turnover on such securities. Once the loan is closed, the note is repaid.
The blank type of bills provides for the existence of a trade transaction. The thing is that the cost of a product or service may not be established immediately. In addition, sometimes the final cost simply changes. Therefore, the buyer in this particular case can trust the seller. He certifies a separate form with a signature (without filling it out). And the seller himself will fill out the fields of this form.
Well, a financial bill is needed for a lending scheme between enterprises. We already looked at how this works a little higher. A standard bill of exchange is needed in order to secure a transaction between the buyer and the seller. An avalized security is needed in order to obtain additional guarantees for the fulfillment of an obligation (making a payment). Avalized bills can combine varieties of others. The key factor here is the presence of an avalist. This is a banking organization that participates in the scheme.
In addition, bills of exchange can be used as a subject of sale and purchase. Sometimes promissory notes are used to post collateral. The essence of a bill is that you can use it to enter into purchase and sale transactions. The presence of a bill of exchange in such a scheme eliminates the possibility of prepayment.

How to find out the main and penalty periods for storing property in a pawnshop?
There is a basic shelf life for gold or other valuables in a pawnshop. It can be different - it depends on the value of the thing. It is established according to the rules of the pawnshop at the time of concluding an agreement with the client.
As a rule, the main period is in most situations from 1 month to 1 year.
Any pawnshop also, according to the contract, offers a certain period on top of the main one, when interest is still accrued, albeit increased. During this time, the pawnshop is still waiting for its client to return to redeem the pawned item.
If all the deadlines have passed: both the main and additional ones, then the pawnshop has the right to assume that the person has finally pawned his item, received his money and will no longer return for redemption. From this time on, the pawnshop fully owns the pledged property and can dispose of it as it pleases. In most situations, the pledged property is put up for public auction or sold through partner outlets.
The main document, which precisely specifies the terms for the redemption of property, as well as daily interest for storage in a pawnshop, is the contract. The contract is concluded at the moment of delivery of the property between the pawnshop (its representative represented by a specialist appraiser) and the person transferring his rights to the item, car or real estate.
Bills of exchange from the perspective of Russian legislation
So, we have learned about what a bill of exchange is. We learned about how guaranteeing a bill or check works. But all this is not enough. Now we need to understand how bill accounting works on the territory of the Russian Federation. After all, the general theory is of course good. But the topic itself requires consideration of the issue from the perspective of Russian legislation.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the term bill of exchange is not included in the legislative regulations. To be more precise, the interpretation of the term itself is not determined at the level of current legislation. It is also interesting that the term was originally interpreted. Just in that very letter from the Central Bank of Russia, for 1991. It was at that time that it was indicated that a bill of exchange is an obligation in monetary form, which is not conditioned by anything. And this obligation is provided along the following route:
- From one subject of legal relations to another.
- From the drawer to the holder.
This letter, as you understand, has long lost its power. In fact, in modern times, all bills of exchange can be classified according to the method of calculating the interest rate on the debt:
- Discount.
- Percent.
If we are talking about a specific area where the turnover of such securities occurs, then bills can also be distinguished into the following categories:
- Commodity and financial.
- Treasury.
- Banking.
And now we need to talk about the form of the details. It is strictly regulated in Russia. However, in other countries the situation is no better.
An obligation in the form of a bill of exchange can only be based on a document. This is regulated in 48 Federal Laws. The form for details was developed and established back in 1937 on the territory of the USSR. And apparently, the form of the bill has not changed much since then.
So, the mandatory details of such a security are:
- Tags.
- Denomination
- Name.
- Payment term.
- Place of payment.
- Recipient details.
- Place of compilation.
- Date of preparation.
- Signature.
A bill of exchange mark is a classic designation of a document. Those. the label in our case will be the inscription “bill”. This is a document designation and must be present. The face value is the amount for which a security is issued. The name of the payer is relevant only for securities of the transferable category. But the due date is the moment by which the paper will have to be repaid. We have already talked about what will happen if you break this rule.
The place of payment is also indicated. And also an indication of the recipient. In particular, these details indicate the party that generates the order for payment. The party may also be designated simply as the addressee of the payment. Next, indicate the place of issue of the security and the date. At the end, the drawer must affix his signature. That's it, this is where the list of required details generally ends.
Practice has shown that some papers can be used according to the replenishment model. In other words, the place and date of the obligation may not be initially included in the form. This is just a blank type of bill. And if necessary (later), the conditions can be replenished.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, several legal acts are used that regulate the circulation of such securities:
- Decree of 1937 (USSR).
- Federal Law 48.
- Constitutional norms of the Russian Federation.
- International Law (1930 Convention).
In fact, nothing has really changed since the 30-40s of the last century. If we are talking about bills.
We can say that bill circulation in modern Russia is regulated not only by domestic, but also by supranational legislation and regulations.
At the same time, it is still not worth denying the obvious problems of using such securities on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Using promissory notes you can hide profits from the tax service. They can be used to hide funds and turnover from the taxation system. Which, as you understand, hardly suits legislators and tax officials.
In addition, there are a lot of financial securities in circulation that did not arise from actual needs, justified by industrial and commercial turnover. Not at all, we are talking here rather about the mobilization of the money supply on the market. And not in one market, but in all of them at once. In addition, assessing the reality of the transaction is not as simple as it might seem. And fictitious securities are possible even in modern reality. And this leads to the fact that the issue gives rise to a large number of bills without real collateral.
In some situations, bills of exchange can also be used as a tool used for black or gray turnover. The whole point is that the proportional scheme of economic turnover may be violated here. Which, as you understand, against the backdrop of real restrictions in commercial lending, may prompt the parties to use securities for other purposes.

What to do if you miss a loan payment
We remind you that there are no mandatory monthly payments in one amount or another in our pawnshops. When using a loan, you pay only interest, and even this is calculated daily, not monthly. In other words, having received a loan from a pawnshop and using it for, for example, 18 days, it is during this period that you need to pay interest and then return the loan amount issued if you would like to buy back your gold again. Your financial obligations to the pawnshop end here.
- There are no fines or penalties for late payment
- Hidden fees – no
Another convenience: you can partially repay the loan amount, thereby changing the amount of interest accrued - they will be recalculated for the amount remaining in use, and not for the entire loan amount.
For maximum convenience for borrowers, the agreement provides for an automatic extension of the loan term. This means that at the end of the document’s validity period, you do not need to collect documents and renew it; the pawnshop’s employees will do this, of course, with prior approval of such a need.
How does automatic extension of the loan term work?
In many respects, our pawnshops compare favorably with banks that provide loans - for example, the convenience of prolonging a loan and an agreement on it is much more convenient in the Pledge of Success network. Step by step it looks like this:
- You took out a loan for two months;
- We paid interest for the first month, then for the second;
- After paying interest, the loan is automatically (if necessary) extended by the pawnshop for another month
If you are ready to buy back your gold, simply deposit the deposit amount at the pawnshop’s cash desk or pay by bank transfer through your personal account.
This convenient system can be used for a whole year. Moreover, the Pledge of Success pawnshops have preferential programs under which interest on loans is minimal or non-existent.
We draw your attention once again: at any time,
without penalties or interest,
you
can receive gold pledged in any of the pawnshops in our network.
Of course, if the owner of the jewelry does not pay interest on the loan for a long time and/or does not respond to requests from our specialists, the pawnshop has the right to dispose of the retained collateral at its own discretion. The period after which the gold becomes the property of pawnshops, unless the pledgor informs otherwise, is always specified in the loan agreement.
About the forms of the endorsement in the bill of exchange
Well, now a little about what kind of endorsements there are in the context of the circulation of bills.
So, there are several forms of transfer of a bill. One of them is through an endorsement. Such an inscription is called an endorsement. This is an inscription that reveals an order of an unconditional nature. This order reflects:
- Full transfer of rights.
- Possibility of receiving payment for a security.
Sounds simple? Yes, but in practice, the scheme itself is a little complicated. In fact, conditionality in relation to endorsement is categorically excluded. Because it uses the scheme of an unconditional obligation in the document itself. It will not be possible to partially transfer the amount of the bill by endorsement. Therefore, the endorsement cannot be partial. The transferring party must install the endorsement in his own hand and sign it without fail.
At the same time, the endorser (i.e., the transferring party) can even relieve responsibility for payment and acceptance. But you need to mark the appropriate content; without it, liability will be imposed automatically and by default. But the impact of excluding the endorser from the chain of obligations will be noticeable. After all, the liquidity of the security in this case will collapse. And such paper can only be transferred through a purchase and sale transaction. And the deal will have to be accompanied by a full-fledged monetary policy agreement.
And now about how to cash bills. And what to do if you invested money in a bill, but it was not returned. On the question of whether companies can cheat with bills of exchange. Of course they can, in general, a bill of exchange is one of the most promising tools for withdrawing funds from clients.
What can you pledge?
To apply for a loan from a pawnshop on collateral, you must first clarify which organizations and what they accept. There are institutions that are ready to issue money for various valuable things, and there are companies that accept, for example, exclusively gold and silver.
The main list of items that you can pledge to get money:
- Jewelry made of gold and silver.
- Vehicles.
- Expensive dishes.
- Laptops, computers, phones and other electronics.
- Antique things.
- Appliances.
The highest priority collateral items from this list are gold and silver. They are accepted in almost all institutions.
About scammers and ways to earn income
Let's start with the basic situation. The fact is that such securities can be sold (sold) under the following conditions:
- The price varies.
- The amount of debt obligations is one.
And this is very actively used in the stock markets. Conventionally, someone could sell a security that includes $150,000 in liabilities. Despite the fact that the price of the paper itself will be 140 or even 130 thousand. Doesn't the logic add up? Everything is a little more interesting.
First, the seller may be a traditional reseller. This is how bills of exchange are purchased from a bank. This is usually not a bearer bill, but an unnamed security. And the seller could purchase a whole package of such illiquid “goods” from a banking organization. For a conditional 100 thousand US dollars. And if the transaction goes through (which most likely will happen), the seller will receive a direct profit. But history is silent about what the buyer will do in the end.
If you purchased a standard bill of exchange from a banking organization, then you can receive a profit only after 5 years. This already allows you to transfer this paper through chains of holders. This is a non-registered (not recta) bill of exchange, and you can do whatever you want with it. And the chain of resale of a security can reach enormous distances.
Let's say you were sold a security for $130,000. The seller urgently needed funds and was not ready to wait another 3.5 years. And you purchase a bill. And now you have to wait for the moment of repayment.
The trick is that the paper can be compromised. In other words, the bill may be fictitious. Perhaps neither party provided any funds. This happens all the time on the market. After all, a transaction for the supply of something is often hidden under a bill of exchange. And in fact, what you have in your hands is not so much a security as a transaction. This diagram provides a whole scenario:
- Party A transfers funds.
- Party B issues a bill.
It seems that everything is simple and clear, but this is only at the beginning. Indeed, often, instead of cash, a specific security is transferred. And here the whole essence of the scheme is revealed. After all, a security like a bill of exchange may not have the equivalent of a real monetary amount. Let's assume that the deal was concluded for a conditional 200 thousand rubles. But he just turned to a third-party customer. And it is for this reason that bills usually provide for a much higher amount of cash.
Purely theoretically, a registered bill of exchange can also be sold. But this is in theory, but in practice it will be very problematic to implement something similar.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, there are usually several scenarios for how one can cheat on the market.
What happens if a person bought bills through a company? He may not even know that the company had other plans for this security. The company simply decided with the help of a bill of exchange:
- Sell the obligation.
- Pay for it.
And the company initially knows that this security is fictitious. Because the banking organization simply will not pay anything on this security.
This creates a very simple scheme, with fraud on both sides. This is already a deception of a professional scale, it should be noted right away.
And a banking organization may simply refuse to pay funds to the bill-holder company. This creates additional risks. In this case, you will have to submit your claims through the courts. The subsequent holder retains this right.
Events take a completely different turn in a situation where a bank representative acts as a fraudster. In this case, the holder does not receive his funds. And in fact, it is not uncommon for a request for payment to be followed by a direct refusal from the financial institution. And sometimes the banking organization itself simply disappears.
However, today banks do not engage in such primitive schemes. Typically, deception occurs in complex systems, and it is not always possible to even qualify fraud. Despite the fact that the holder’s deception is obvious to everyone.
Let's look at the issue with the bank. It will be of interest to many.

Scheme of deception on bills of exchange by a banking organization
This is where the field for open manipulation begins. Because if the fraudulent scheme initially involved the participation of the bank as one of the interested parties, it will be difficult to determine the fraud. Indeed, in fact, the following situation may arise:
- Side A sends you to Side B.
- Side B refers you to Side A.
And most importantly, no one “has” the information. What to do in this situation? Well, for starters, don't panic. Because panic in this matter has never helped anyone. But she only did harm.
The right decision would be to contact a professional lawyer. And together with a lawyer, you can start collecting evidence. After this, you go to court. If it is possible (at first glance) to recognize fraud in the scheme, then you must also contact law enforcement agencies.
If we consider the situation with the police, then everything is simple and complex at the same time. Because in such cases, a full investigation is usually not carried out.
But in the case of litigation through court, the chances are greater. Simply because the claims will be quite obvious. You demand payment of a bill. And you can file a claim against both the company and the banking organization. In the case of a criminal case, in most cases it will not be opened. Because in an obviously fraudulent scheme, a system of “bypassing the law” is most likely used. Those. parties involved in fraud are simply circumventing current legislation. And bringing the perpetrators to real criminal responsibility will not be as easy as it seemed at first.
In the case of fraud on the part of a banking organization, you also need to determine the real state of affairs. After all, the injured party cannot always correctly interpret what is happening. And this is a very important component in such matters. Information about a transaction is not always true. And there are several different options possible:
- The funds were accepted by the banking organization.
- The funds were not accepted by the financial institution.
Let's denote the bank as A and the company as B. To simplify the diagram. And let's go from the opposite. Party B claims that A accepted the funds. Despite the fact that the bank did not accept any funds. In this case, perhaps there was not even any bill of exchange. Because usually banking organizations do not issue securities without cash backing. Most likely the security is counterfeit. This means that there is a real fraud that must be investigated by the relevant law enforcement agencies.
If the banking organization actually accepted funds, then a new question arises. Perhaps the representative of Party A is simply trying to lead the victim on the wrong trail. Because it will be easier to prove the receipt of funds in this case. A bank is not a “careless” organization that can hide anything at all.
But even here, not everything is as simple as it might seem initially. It is not always possible to track transactions. Yes, even in the modern era of widespread digitalization. And if the bank’s representatives also begin to develop their own line of defense in court, then they will not be able to prove anything at the first or second instance. We'll have to take the matter to higher authorities. But not everyone may have enough time and energy for this. So here, too, everything is not as simple as it might seem initially.
If there is a fact that the bill has not been paid, perhaps the security itself simply does not exist. And this is a serious problem in a situation where this is revealed. After all, the client is literally “suspended” in the air. And he doesn’t always understand what to do.
Deception schemes in other countries
As you understand, such a security as a bill of exchange can become a very destructive instrument in the right hands. Especially if we are talking about fictitious or obviously counterfeit papers. However, you can do whatever you want with genuine ones. In the USA there is a very cunning scheme that allows you to literally ruin companies. In part, this scheme has already been implemented on the territory of the Russian Federation, but not to the same extent.
John Doe is a designation for the male party in lawsuits. This designation is available in the States and England. We have no analogues like this. So let’s imagine that a certain Doe family uses the services of its consultants. This is a very wealthy family, so without consultants they simply will not be able to exist normally and save their savings. So, over 4 years, the Doe family spent a total of 9-12 million US dollars just to pay for such “helpers”. But they still could not avoid fraud with bills.
Everything is very simple. There was one very interesting person on the consulting staff. He began to advise his clients the following scheme:
- We transfer assets to offshore companies.
- We receive payments every year.
This scheme allows you to avoid one of the taxes. And in the US, taxes are a serious problem for wealthy citizens. It is in Russia that they are trying to maintain appearances by increasing personal income tax to 15% for some categories of the population. Which, in essence, doesn’t really do anything. In the States, taxes are something that everyone feels literally physically. And they fear tax officials more than the police. But that's not what this is about.
The Doe family listened to their advisor and began setting up trusts. As a result, a whole network appeared. There was just one problem. To avoid taxation, trusts had to be transferred to trustees. And I had to do this. And everything in this scheme would be clean. If not for one thing. This is the human factor. One of the managers turned out to be the “hole” in this whole monstrous ship. Because he registered 5 trusts at once. But he did not deposit cash. He used promissory notes. The same bills that were never paid.
The matter came to a direct conflict with representatives of the authorities of the offshore zone. Subsequently, this manager will of course be discovered and even certain sanctions will be applied to him. But the situation could no longer be reversed. Everything was done in such a way that it would not have been possible to correct what had happened. In Russia, the peak of bill fraud occurred in the period 1990-2000. Then the volume of cases gradually decreased. But even today you can fall into the trap of scammers.
How to rob a company?
In Russia, deception schemes through bills of exchange have always been quite primitive. You can choose a more obscene term, but it’s better not to use it. So, our bills can also be used for more complex fraudulent schemes.
Remember at the very beginning we dealt with the fact that friendly bills are prohibited in our country? Now you will find out why they were banned from circulation. In fact, any fraudulent scheme using such securities is distinguished by two nuances:
- It's very easy to do something like this.
- It is extremely difficult to recognize fraudulent activities.
Let's look at one simple diagram. In fact, it involves the withdrawal of real security from the company. From the mass of property of a specific company. Which, as you understand, is a very promising direction. And profitable on top of everything else.
To implement such a fraudulent scheme, you will have to create duplicates of genuine securities. A certain number of real bills of exchange may be registered in the company's property. The company employs hired managers. Most often, they are the ones who begin to start this kind of fraud. How to do this? Everything is extremely simple:
- We need a front company.
- You need an agreement on the exchange of securities with a laying company.
Then it's a matter of technology. A shell company costs a few pennies. And the profit from the fraudulent operation is huge. Through a shell company they begin to exchange genuine papers for counterfeit ones. The dummy paper can then be resold to the next party. The installment plan for such securities is rarely less than 10 years.
This whole scheme involves another shell company, the presence of which is not always obvious during investigation. Because it is through the second “fulcrum” that “sabotage” will be carried out. Because the debt obligation will not be fulfilled. And the original bill literally “floated away in an unknown direction.”
The company receives some new debtor, with a very dubious origin.
The scheme itself with resale and debt obligations is only needed to cover up the crime. Because finding fault with the design methods will be problematic. The third company is in hiding; for the time being, no one even suspects its existence. It is very difficult to open such a scheme.
Practice has shown that representatives of the injured party find out about fraud too late. Usually when the team changes. And most importantly, the accountant changes. A new specialist comes to the workplace and discovers strange debt obligations. Starts checking. And here the scale of the theft is revealed. At the same time, unraveling this entire system will be problematic. After all, all the papers are not fake bills, but real ones.











