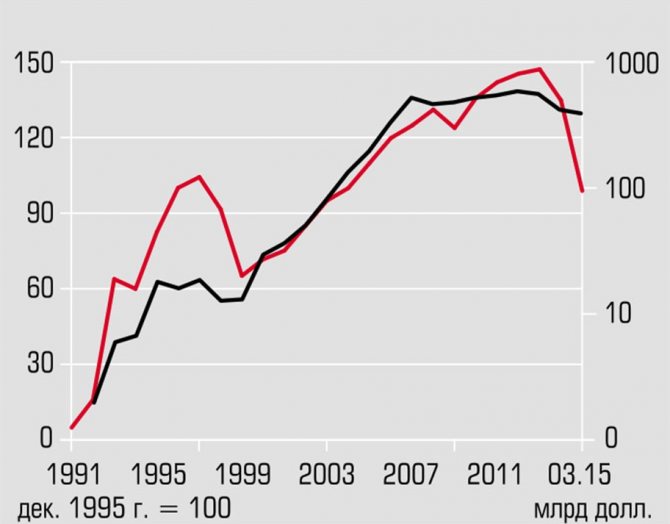
The title of reserve currency is assigned to the American dollar and is confirmed by the fact that the bulk of trading on stock exchanges and international trade transactions in the world are carried out in American currency.
All money of modern states is hung with certificates and confirmed by everything possible. But in reality they are only socially recognized pieces of paper. That is, pieces of paper in which people see value. Stop people recognizing their value and they will lose it. Russia experienced two revolutions at the beginning of the 20th century, during which many different types of money appeared, but all of them also instantly lost value. Our mind contains a link between money and industry, gold reserves, and the like. For money to be recognized as valuable, it must be tied to something. This binding is just proof of their value..
What is the strength of the dollar and euro?
The success of the dollar is the result of work that lasted many decades. This work consisted of powerful propaganda of the American way of life, as well as the systematic and stubborn pushing of the dollar into the economies of other countries. Then the topic of globalization, world economic interests and mechanisms, otherwise called globalization, arose. Under these conditions, the world began to need a single global savings currency that would be recognized in all countries.
However, one should not think that this happened by itself, much less thanks to the success of the American economy or the military industry. The Americans spent a lot of money and effort to promote their currency and achieve this global recognition.
The people who manage these currencies well understand the main principle that the value of money is in its recognition. Not in industry, not in economics, but specifically in recognition. Although, of course, industry and economics simplify the recognition procedure.
Why did the Central Bank launch the machine?
Experts differ on this issue. Some believe that in this way the Central Bank is trying to create a certain economic cushion. In simple words - so as not to print out reserves and not waste money from various funds. It’s easier for the state to turn on the machine and print more money. Of course, no one knows how the global economic crisis and pandemic will develop further. Most likely, the decision was made to let go of inflation rather than spend reserve money. It is difficult to say what such a decision will lead to. In any case, nothing good should be expected, experts say. If we talk about the crisis of 2015, then the problems were completely different. At that time, there was no global pandemic and the processes that accompany it. The pandemic has affected almost all states and the global economy. Now the situation is somewhat more complicated than it was five years ago. The Central Bank itself makes an excuse and explains this issue of money by the fact that the population’s demand for paper cash has increased. Of course, most of the population managed to withdraw money back in the spring of this year. Many citizens plan to keep their savings “under the mattress” rather than in banks or securities.
What is our Russian ruble backed by?
They say that gold, oil, gas, timber, etc. It's not really clear. Perhaps neither the ruble, nor the yuan, nor the euro, nor the West African franc are backed by any gold. And what?
The Russian ruble is backed by the promises and convictions of the president and prime minister, as well as those standing next to them. Many people scold and dislike Putin, but Russia believes in him. And he talks about the very value of our ruble.
Simply put, it seems that there are practically no currencies in the world that are backed by something.
Russian ruble: economics
The Russian ruble is the monetary unit of Russia. Unit of measurement: 1 ruble = 100 kopecks. Letter designation – RUB. ISO standard - numeric code 643.
Economics of the ruble
The Russian ruble has a rich history of ups and downs. Among the most important events in the life of a currency, it is worth highlighting:
- 1895-1897 - the ruble was securely attached to the gold standard, which lasted until 1914. The currency was exchanged at the rate of 1 ruble = 0.774 grams of gold. During this period, the Russian economy was on the rise - industry was modernized, new factories appeared, business activity developed, GDP grew, railways were built, and so on;
- 1914 - the exchange of rubles for gold was stopped. “Nikolaev chervonetsy” went out of use. More and more money was issued to offset military expenses. Since the beginning of 1914, there were already more than two billion rubles in circulation, and by 1916 - already more than eight billion.
- 1917 - the volume of money issued is constantly growing. One of the largest banknotes is the “Kerenka” (1000 rubles);
- 1919 - the release of the so-called “Sovznak” began. By 1922, their rate jumped 10 thousand times, and by 1923 – 100 thousand times.
To reinforce faith in the currency (during the NEP period), parallel money was issued (it was backed by gold). The exchange was carried out in the following ratio - 1 gold ruble = 50,000 sovznak. In general, the ruble exchange rate fell 50 billion times;
- 1928 - the ruble, backed by gold, made it possible to return the economy to operation;
- 1932 - constant “cleansing” of the private sector led to new problems with the currency - it stopped being exchanged for gold;
- 1938 - the inscription about the gold content disappeared from the money. But another inscription appeared confirming the provision of rubles “with all the property of the USSR”;
- 1947 - monetary reform, confiscation of funds. The population's deposits have been cut. If there is an amount of 3,000 rubles or more - by a third, more than 10 thousand rubles - by two thirds;
— 1961 – powerful denomination and devaluation. The exchange is made in a ratio of 10:1;
- 1992 - the economy of the old ruble collapsed, the printing of a new currency began. The Russian government took up the matter. The printing press went into action. Hyperinflation began;
— 1993 – confiscation reform (replacing old money with new ones). The first limit is 35 thousand rubles, later – 100 thousand rubles;
- 1997 - Russians became “millionaires”, but even with a million you can buy little;
— 1998 – new denomination (three zeros were removed);
- August 17, 1998 - default.
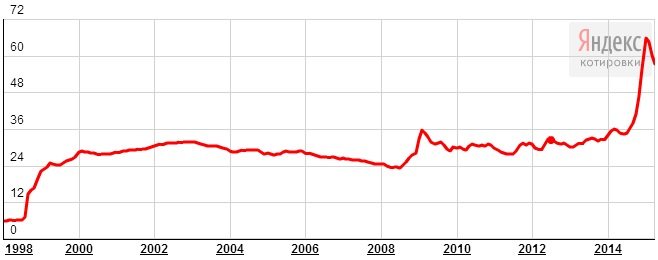
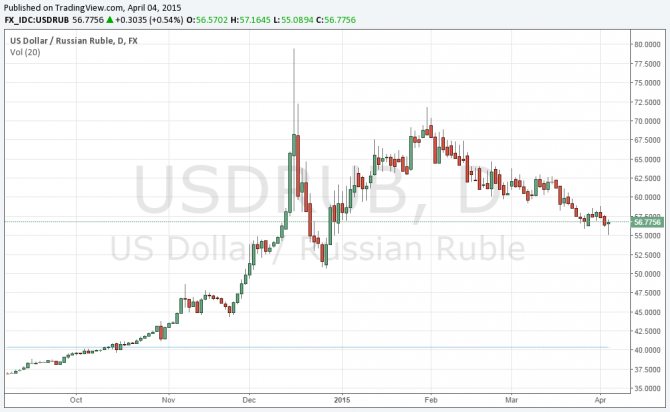
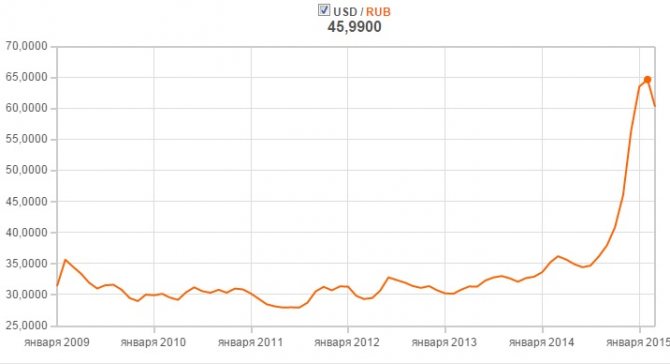
In 1998, the ruble exchange rate against the dollar was 5.99 rubles, in February 2000 - 28 rubles, in February 2009 - 35 rubles. From June 2014 to January 2015, the ruble to dollar exchange rate fell from 34 to 65. In April 2015, the rate stabilized at around 57 rubles.
How much is a ruble worth?
The Russian ruble is the official currency. Its task is to ensure settlement procedures within the country. When making transactions with other countries, the key factor in the value of money is its exchange rate.
The ruble exchange rate is set by order of the Central Bank every working day. The declared exchange rate is taken into account from the next calendar day (from the moment of approval) and is valid until the receipt of a new order from the Central Bank. The Bank of Russia has established a strict list of currencies in relation to which official rates are established.
The US dollar to ruble exchange rate is calculated by the Bank of Russia. The basis is data from Moscow Exchange quotes. The calculation itself is carried out according to a special methodology compiled and approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Calculation of other exchange rates is carried out taking into account the US dollar exchange rate on the interbank and international currency markets. The official US dollar rates set by the central banks of other countries are also used.
Official rates of other countries included in the monetary and economic union are rates calculated on the basis of the euro/ruble pair (the rate of the latter is set by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation using calculation coefficients).
Determining exchange rates is a complex process influenced by many factors:
— inflation rate; — difference in interest rates; - the balance of payments; — features of the foreign exchange market (presence of speculation); — timely payment of international debts; — level of confidence in the currency; — features of the country’s monetary policy; - political situation; - natural disasters.
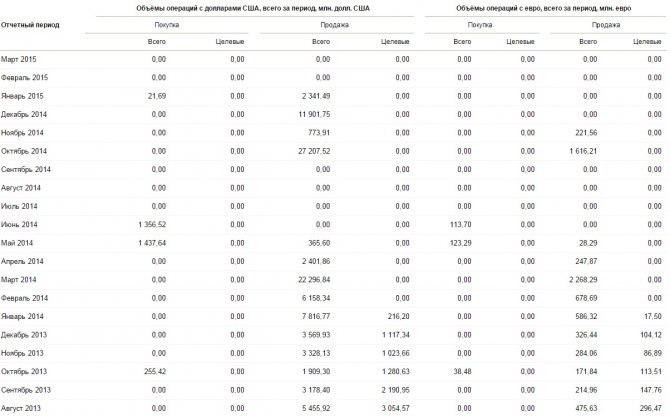
Currency intervention is maintaining a stable ruble exchange rate by buying (selling) large volumes of foreign money. When the ruble exchange rate decreases, the central bank buys the national currency, and when it increases, it sells it. During December 2014, about 12 billion dollars were sold. Today, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation does not carry out foreign exchange interventions, that is, the ruble exchange rate changes under the influence of market factors.
The Central Bank pursues an exchange rate policy in relation to the national currency exchange rate. In case of sudden changes in the exchange rate, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation reserves the right to intervene in the process and smooth out strong changes. In this case, there are no fixed course restrictions.
The main operational benchmark for the Central Bank is the euro/dollar bi-currency basket (0.45/0.55). The limits of possible exchange rate changes depend on the volume of interventions in the foreign exchange market.
The limits of the operational interval change automatically as soon as the volumes of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation reach the required value.
Since the end of 2013, the following scheme has been in operation. As soon as the volume of sales or purchases of foreign money by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation reaches 350 million US dollars, the boundaries shift by five kopecks up or down, respectively.
Reducing volatility is achieved by setting a changing operational interval. It has several ranges, each with its own permissible volume of interventions. There is a “neutral” range in which foreign exchange interventions do not occur. The closer the value of the ruble is to the borders of the bi-currency basket, the more transactions with foreign currency the Bank of Russia makes. This method smoothes out volatility.
Target investment is a parameter used to calculate the total amount of intervention in order to shift the upper (lower) limit. If the volume of Central Bank interventions during the day exceeds the volume of target investments, then the resulting difference is used for subsequent adjustment of limits. This can happen on that day or the next day (when the limit value is reached).
Since the beginning of 2014, targeted investments in Russia are 0 US dollars per day. This can be clearly seen from the statistics above.
What to do with rubles?
The devaluation of the national currency makes you think about the fate of your savings. What to do in this case with the ruble? There are several options:
1. Dollars. After a sharp devaluation, the ruble exchange rate stabilized. This is a great chance to buy currency. There is the following trend. The decline in oil prices led to a fall in the exchange rate of the national currency. Further price increases did not stabilize the situation. On the contrary, the ruble exchange rate continued to fall. Against the backdrop of negotiations on Iran and the likelihood of large volumes of oil spilling onto the market, buying dollars is one of the best options. There are no prospects for the ruble to strengthen in the future. But simply holding the currency will not have an effect - it must be bought cheaper and sold more expensive. You don’t have to deal with cash – work on the stock exchange.
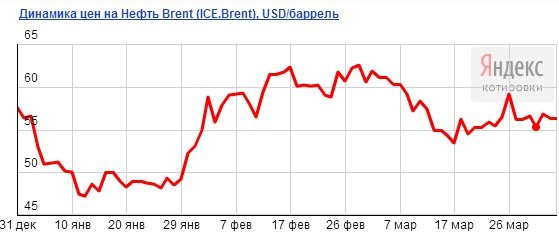
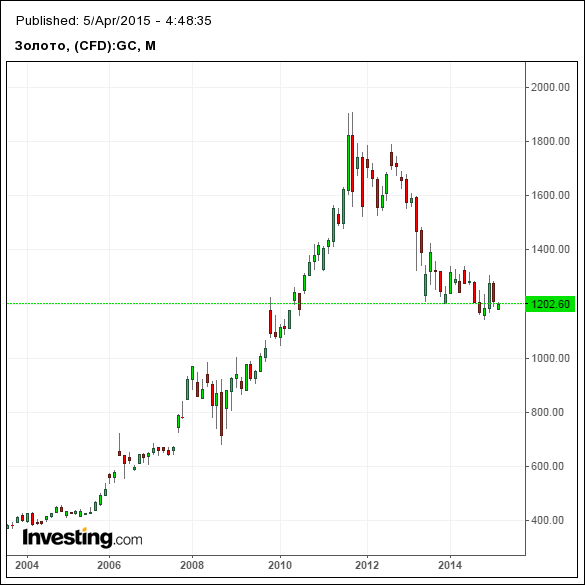
2. Gold. The trend of investing in gold still continues, but experienced investors are refusing this idea. There are several reasons:
— there is a danger of a further decline in gold prices; - an investment can only yield profit in the long term.
If you are going to invest in precious metals, it is better to invest in palladium. This metal is considered more stable for residents of the Russian Federation.
3. Taking out a car or real estate loan is a dangerous option. The depreciation of the ruble leads to a decrease in the purchasing power of people. Housing prices are inflated and will decline over time. Applying for a loan is an overpayment that cannot be covered by potential profits. A period of instability is dangerous because of the prospect of losing your only source of income. According to forecasts, real estate prices will decrease in the second half of 2015.
4. Investing in material assets is not an option. In December 2014, hardware stores were overcrowded as people bought everything to save their savings. As soon as everything calmed down, attempts to sell the equipment were unsuccessful. The reason is a decrease in purchasing power. You have to sell at a price lower than the purchase price. If you have small savings, leave them - this is an opportunity to calmly survive the crisis.
5. Mutual funds, shares, work on the stock exchange. The best option, but the most labor-intensive. It is important to keep abreast of events, monitor stock prices, and learn how to invest wisely.
Is there a risk of default? There is a probability of default in Russia, but it is about 5%. This depends on a number of factors - government policy, the presence of sanctions, credit rating indicators and insurance against default.
Ruble and dollar: when to buy and sell? There are several options:
- the ruble is devaluing - you can’t buy dollars; - the ruble is strengthening - time to buy currency. The main thing is the reason for the appreciation of the currency: - the country has changed its vector of development (changed its foreign policy). In this case, there is a tendency for further strengthening; — the strengthening of the ruble is based on the actions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Here the effect is short-term and there remains a danger of further growth of the currency.
Deposits in rubles
Storing rubles at home “under the pillow” is dangerous and pointless. Many people take money to the bank and risk it twice:
— devaluation may exceed the interest on the deposit; - the bank will be deprived of its license and will be classified as problematic.
State guarantees of deposits exist and work, but if there is a significant “swing” in the financial system, there may not be enough funds to cover deposits.
On the other hand, a deposit in a bank is a lesser evil if you have certain funds and are unable to handle them. The main thing is to follow three rules:
1) Check the reliability of the bank (focusing on the rate is a mistake). At risk:
— banks that are already under sanctions; — banks that may be subject to sanctions. Their owners are current leaders or people related to the country's leadership; - state banks; — banks with foreign capital (high probability of investors leaving the market); — small regional institutions.
2) Open deposits in different banks and ensure that the total amount as a percentage does not exceed the amount guaranteed by the state.
3) Give preference to short-term deposits (up to three months). If the situation improves, the deposit is extended, and if the situation worsens, it is withdrawn.
History and relations of the ruble/dollar
The history of the relationship between the ruble and the dollar dates back to the end of the 19th century:
- 1792 - Coin Act establishing the value of the dollar in the amount of 1.6 grams of gold. Converted to grains – 24.75. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 1.39;
- 1834-1896 - the gold content of the dollar decreased to 1.5 grams. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 1.3;
- 1897 - monetary reform in Russia. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 1.94;
- 1916 - inflation after the First World War. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 6.7;
- 1917 - Ruble to dollar exchange rate - 11;
- 1918 - Civil War, devastation. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 31.25;
— 1919-1923 – continued decline in the exchange rate from 72.46 to 2,352,941;
- 1924 - monetary reform. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 2.22;
- 1934 - the gold content in the US dollar was reduced to 0.88 grams. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 1.24;
— 1935 – the beginning of the devaluation of the ruble against the dollar;
— 1936 – the ruble to dollar exchange rate reached 5;
— 1937-1950 — the ruble is calculated based on the US dollar. The volume of gold content is 0.167674 grams. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 5.3;
— 1950-1960 – cancellation of the calculation of the ruble against the US dollar. The ruble became backed by gold. Gold content – 0.222 grams. Ruble to dollar exchange rate – 4;
— 1961-1971 - Khrushchev's monetary reform. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 0.9;
- 1972 - devaluation of the ruble. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 0.829;
- 1973 - The Gold Standard was abolished in the USA. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 0.826;
— 1976 – the Jamaican system began to operate. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 0.758;
— 1977-1990 the ruble exchange rate against the dollar was in the range of 0.6-0.7;
- 1991 - commercial rate - 1.75 rubles. for one US dollar, on the “black market” - up to 32-33 rubles;
- 1992, August 1 - a free exchange rate was introduced. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 125;
— beginning of 1994, the ruble to dollar exchange rate was already 781;
- October 11, 1994 - sharp devaluation of the ruble, “Black Tuesday”. The ruble exchange rate soared to 3,926 rubles per dollar;
- 1997 - for one dollar they give 5562 rubles;
- 1998, January 1 - denomination. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 5.6;
— 1998, September 9. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 20.8 (post-default tide);
- 1998, September 15 - maximum “low tide” to the rate of 8.67;

— 1999-2003 – constant growth of the exchange rate to 31.78 rubles;
- 2003, September 9 - the highest dollar exchange rate after the default - 31.88;
- 2009, February 19 - the maximum dollar exchange rate this year. Lasted with hesitation until September 13, 2014;
- 2014, September 13 - the 2009 record was broken. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 37.65;
- 2014, December 18 - maximum denomination of the ruble. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 67.78;
— 2015, April 04. The ruble to dollar exchange rate is 56.75.
Ruble on Forex
Freely convertible - a currency that has no restrictions when making payments or moving capital from country to country. Today there are 17 freely convertible currencies. Russia is not among them.
This is one of the reasons why there was no ruble on the forex market until February 11, 2013. By the way, even today it is not very popular.
Popular pairs are EUR/RUB and USD/RUB. What is special about working with them?
Among the advantages:
— excellent intraday price movements and high volatility. This is a chance to make quick money in intraday trading. The main thing is to choose a broker with a changing (floating) spread;
— pairs EUR/RUB and USD/RUB are easy to predict, because the country’s economy and its political “games” are before our eyes. For successful trading, it is important to follow economic and political news feeds not only in the Russian Federation, but also abroad;
— the ability to work on a ruble account. This is the best option for a beginner: minimal leverage, good spread, small requirements for starting capital;
Disadvantages:
— you can work with EUR/RUB and USD/RUB pairs only during the Moscow Exchange, that is, from 09:00 to 20:00. When creating your system, it is important to take this into account first. By the end of the week, the open position should be closed;
— a limited list of currencies with which the Russian ruble works on Forex; — low interest in currency. Trading on the EUR/RUB and USD/RUB currency pairs is essentially done with a broker.
The most popular pair is USD/RUB. Its features:
— the pair is actively traded on the Moscow Exchange during business hours. After the stock exchange closes, a “saw” appears on the chart. On the night from 00.00 to 08.00, it is better to close trading on USD/RUB;
- an increase in the refinancing rate leads to a decrease in the exchange rate (and vice versa);
— economic and political news can greatly influence changes in the dynamics of USD/RUB;
— the dynamics of the pair’s price movement depends on the price of oil.
Today, trading with EUR/RUB and USD/RUB pairs looks unpredictable, but experienced traders find the opportunity to play on sharp fluctuations and anticipate rate changes.
Ruble in the world
The Russian ruble has a weak position in the world market. In December 2014, after a sharp drop in exchange rate, the ruble was named the weakest currency in the world. Sanctions, lower oil prices, and the economic situation in the world are putting pressure on the national currency. But starting from February 6, 2015, the ruble exchange rate has been growing. Today, one dollar already gives 56.75 versus 66 rubles on 02/06/15.
The well-known publication Bloomberg named the ruble one of the best currencies for the carry trade strategy. The meaning of the “carry trade” is simple - a loan is taken in the national currency of a country where minimum interest rates are established, and invested in a country with maximum interest rates.
Investors borrow US dollars and invest in ruble assets. For three months of 2015, the profit was more than 9%. This is a high figure that even the Swiss franc cannot boast of. The decline in volatility in recent months has further attracted global investors.
Dynamics of the ruble
Let's look at the dynamics of the ruble against a number of the most popular currencies:
1. American dollar. Currency pair USD/RUB
2. Euro. Currency pair EUR/RUB
3. Canadian dollar. Currency pair CAD/RUB
4. Swiss franc. Currency pair – CHF/RUB
5. Japanese yen. Currency pair – JPY/RUB
6. Australian dollar. Currency pair – AUD/RUB
Thus, recently there has been a clearly noticeable tendency towards the strengthening of the national currency. But whether it will continue depends on many factors.
Will the Central Bank's policy change?
The possible introduction of a digital ruble will change the financial sector and affect money circulation, so it is important to assess the impact of a digital currency on monetary policy (MP), the report says. For example, the reallocation of funds between bank deposits and digital currency will have an impact on bank balance sheets and may also lead to higher rates on bank deposits and loans. In addition, with the advent of digital money, the structural balance of liquidity of the banking sector will also change, the authors of the report list.
According to NES professor Oleg Shibanov, in Russian conditions the possible introduction of a digital ruble is unlikely to affect the policy of the Central Bank. “By and large, this is an analogue of the electronic ruble, which is already present. The only difference is that the digital ruble will be available to companies and households, that is, the Central Bank will communicate not only with banks, but also with ordinary citizens,” he says. The transformation of the financial system in terms of services and digitalization occurs constantly and these processes smoothly penetrate into the main indicators, so monetary policy always has time to adjust, adds Sofya Donets, economist at Renaissance Capital for Russia and the CIS.
Competition between the Central Bank and commercial banks will not arise “on the spot,” since the Central Bank’s rates for placing the digital ruble will be almost zero, Shibanov notes: digital money will more likely compete with cash than with deposits, because with positive rates on deposits, people will still will want to keep their funds in deposits rather than “virtually in a digital cache.” The digital ruble does not mean an additional share issue, the expert adds. Paper money will be exchanged for new currency and thus taken out of circulation.
Deputy Chairman of the Central Bank Alexey Zabotkin, who oversees monetary policy, believes that ultimately the digital ruble will lead to strengthening financial stability. “The presence of a digital ruble will limit the risks of using other, less reliable payment solutions in the digital world. And the creation of additional payment infrastructure for the digital ruble will further help support the reliability and uninterrupted operation of the payment system in the country,” he wrote in a column for the Central Bank’s Econs magazine.
Why do all this if you have cash and cards?
First of all, the Bank of Russia, according to its representative, sees in the introduction of the digital ruble the opportunity to provide citizens and businesses with accessible and fast payment services at minimal costs, as well as the need to create high-tech money for the development of the digital economy and the introduction of financial innovations accessible to everyone without exception.
“On the digital currency platform it will be possible to create new services for citizens, banks, businesses and the state,” adds Tatyana Zharkova. “For example, such a platform can use smart contracts - special programs that automatically check the fulfillment of contract terms and carry out settlements.”
Why does the ruble depend on the dollar?
As we noted above, the Russian ruble is only partially dependent on the American dollar. No not like this. It would be more correct to say that it is not the ruble that depends, but the cost of goods in ruble equivalent. Those goods that we buy almost every day.
Before continuing, I would like to remind our readers that about sixty, or even all seventy percent of the products that we can see on the shelves and racks of stores are imported from abroad. Naturally, we do not buy such goods for rubles. If the products are from China, then we pay for everything in yuan, if from the United States of America, then we pay in dollars, from the European Union - in euros.
Thus, if the ruble weakens against foreign currencies, purchase prices increase. That is why in the last two years the cost of imported goods has almost doubled.
Why does the Central Bank need a new type of currency?
“The Bank of Russia aims to ensure that the monetary circulation system meets the changing needs of citizens and businesses and promotes innovation both in the financial market and in the economy as a whole,” the report explains. The use of advanced technologies in the development of the digital ruble will help reduce settlement costs and increase financial inclusion, and will also open up opportunities for the development of financial services and instruments, the Central Bank believes.
The Central Bank needs the digital ruble to fully control the issue, says Viktor Dostov, Chairman of the Association of Participants in the Electronic Money and Money Transfer Market: “Since banks can now technically issue non-cash money themselves, in theory there is nothing stopping them from drawing any amounts on accounts. Although in practice this has rarely happened, in some malicious bankruptcies, such concerns have been heard for a long time.”
Should you keep money at home?
The key rate of the Central Bank is within the historical minimum – 4.25% per annum. Of course, such a low rate contributes to cheaper loans, but there is also a second side to the coin - bank deposits. Taking into account inflation, if you put money on deposit, you will earn no more than 1.2%. This is the minimum rate for the entire period of existence of the Russian Federation. Ruble deposits do not exceed 4.5% per annum, and inflation is already at 3.8%. In June 2021 alone, Russian citizens withdrew more than 600 million rubles, and the trend remains high. Of course, keeping money “at home” without movement is not the wisest decision, but it is a good option for psychological protection. In this case, citizens feel calm. However, it should be remembered that no one can protect money from inflation, so there is little point in storing funds in this way.
Source>>>
How to get a digital ruble and pay with it?
Citizens and businesses will be able to purchase digital rubles by exchanging them for cash or funds stored in their bank accounts, a representative of the Bank of Russia replies. The possibility of receiving salaries, benefits or other payments in digital rubles is also being considered. All three forms will be freely exchanged for each other.
As the Central Bank explains, you can spend digital rubles in the same way as you currently spend cash or money in a bank account. In online mode, you can use the mobile application; in offline mode, you will need to transfer digital rubles from your online wallet to a mobile phone or other device that supports offline payments without access to the Internet using wireless communication technologies.
Digital rubles can be transferred, for example, in the bank’s mobile application to your account, and then use the card as usual or, if you need cash, withdraw it from an ATM. No modifications will be required either to the cards themselves or to the ATM network for such operations, says Elena Petrova, executive director for development, deputy chairman of the board of Russian Standard Bank.
Conclusion
It's no secret that today the ruble is weaker than ever before . Over the past month, he has been winning back positions, then giving them up again. Surprisingly, oil began to have less of an impact on the exchange rate.
At the moment, one dollar costs a little more than 67 rubles, while a euro costs 76 and a half.
Oil began to depreciate quite a long time ago – for the third year now we have been observing a decline. From 100 dollars a barrel to forty. And yet, why does the ruble depend on the dollar? As soon as oil depreciated, it was necessary to devalue the national currency - it became simply unprofitable to artificially keep it in one place. Thus, it was possible to maintain ruble profits from the sale of hydrocarbons.
What to do to avoid similar situations in the future? Alternatively, you can switch to international transactions in national currency , that is, in rubles. But this is far from being up to us to decide; the authorities will take care of this.
Is it like cryptocurrency?
No, although the digital ruble will likely be built on distributed ledger technology - blockchain. But a platform for digital currencies can also be a centralized IT system. The only FSB-certified blockchain platform at the moment is Masterchain, created by the FinTech Association under the auspices of the Bank of Russia.
“The peculiarity of blockchain networks is that information is duplicated in each of the network nodes,” says Tatyana Zharkova, CEO of the FinTech Association. “This helps ensure data persistence and makes the system more resilient. However, the speed of calculations and settlements on the blockchain is lower than when using a centralized system, since the information must be recorded on many network nodes. At the same time, there are solutions for blockchain settlements that make calculations easier and faster. A number of central banks, when developing a digital currency, propose using a hybrid model that would combine the advantages of different types of systems.”
Why are domestically produced products becoming more expensive?
We have dealt with imported goods. It's time to move on to domestic ones. It would seem that their price should remain at the same level. So why are they also becoming more expensive? What is the reason for this savagery? Do businessmen really want to make money even in such conditions? Of course, everyone wants to get as much money as possible. But this is far from a matter of human greed, no.
Once you dig a little deeper, it will immediately become clear which way the wind is blowing. Domestic products and goods are becoming more expensive because foreign equipment, materials and technologies are used for their production.
Let's say a conveyor belt breaks down - you can't get spare parts for it in Russia, you have to buy them from a supplier outside our state and pay in the same dollars or euros. It's amazing how everything is so interconnected, isn't it?
I only trust cash. Is the digital ruble probably completely unsafe?
“The main feature of cash is that its issuer is the Central Bank, and such money, in fact, is the obligations of the Central Bank,” says Tatyana Zharkova. — Responsibility for the non-cash funds of citizens and businesses stored in accounts in commercial banks lies with the banks themselves. In the case of digital currency, its issuer is the Central Bank. Such funds are accounted for in electronic wallets, which can be managed, for example, using mobile applications - and in this way digital currency is similar to a non-cash form of money. But at the same time, funds in electronic wallets are obligations not of a commercial bank, but of the Central Bank. Therefore, this form of money has fewer risks compared to non-cash ones, since its issuer and guarantor is the Central Bank. In addition, digital currency allows for the convenience of payments that cash does not have.”
“The infrastructure necessary for the circulation of the digital ruble must, of course, be stable, reliable and have the highest level of information security,” says a representative of the Central Bank. “Therefore, the Bank of Russia pays great attention to elaborating such issues to ensure uninterrupted payments and settlements in digital rubles.”










