Both novice amateur archaeologists and seasoned diggers who are thinking about changing their metal detector are concerned with one question: how to choose a metal detector? In a set of often mutually exclusive requirements, how can you find that one device for which you won’t be sorry to pay hard-earned 5-10-100-300 thousand Russian rubles?
Let's try to give a brief overview of popular models and, if not push you to a final choice, then at least set the model search vector.
How the device works

This electronic device is able to detect the presence of metal from a distance and indicate this to a person using a sound alert.
To detect it, it is necessary to influence it using radio waves, then receive a “response” in the form of a secondary signal.
The principle of operation of a metal detector for searching non-ferrous metal is the same for all such devices.
An expensive device differs from a cheap one only in the method of emitting radio waves and the method of responding to a secondary signal-response . Different models differ in the type of signal that notifies about a find.
The metal detector is able to clearly determine which metal is in the field of action of the coil: non-ferrous or black. This significantly saves effort and time .
itself is as follows: alternating current is supplied to the coil, which is the main search element . This creates an electromagnetic field , which spreads, penetrating into the surrounding space. This field does not care about the environment, it is valid in:
- air,
- ground,
- water,
- tree and so on.
If something metal comes into the field of action of the device, eddy currents . They, in turn, attenuate the radiation from the coil. The metal detector picks up this weakening and sends a signal.
Electrical vortices take longer to decay on non-ferrous metals, which is also detected by the device. Therefore, if you set up your metal detector correctly, you will not come across an ordinary rusty prybar, but expensive scrap metal.
Switching search frequency
Modern professional metal detectors have the ability to operate at several frequencies without changing the search sensor. Switching between frequencies occurs in the device menu. For example, in Minelab Equinox, by pressing just one button, you can select the appropriate frequency for the search location: 4, 5, 10, 15, 20 and 40 kHz. The same button turns on the multi-frequency mode.

How to use

The main enemy of effectively using a metal detector to collect non-ferrous scrap is impatience . At first, you will have to learn not only to hear the device’s signals, but also to detect shades. This is necessary to understand the “language” of the device.
A sharp, clear signal indicates something small and well-preserved, such as a coin. A fuzzy signal that is interrupted is a metal object that is irregular in shape and most likely rusty.
The depth of the object will be shown by a bar on the device diagram. A correctly set discriminator will show what kind of metal we are dealing with:
- black
- or colored.
The rules for setting parameters depend on the specific model, so read the instructions carefully.
After reading the manual, you can proceed to practice:
- We choose an uncontaminated plot of land.
- Make sure the soil is soft .
- First you need to work with the discriminator . First, we listen to the soil without an object. Since the metal detector also reacts to minerals, we recognize the degree of mineralization of the soil by sound and set filters that minimize this mineral effect.
- During training, the tonal sound in order to get used to it. But during real searches it is cranked up to the limits of good audibility.
- It is important to keep the reel close to the ground ; it must be moved smoothly and in different directions .
- The coil should not move in a vertical arc - this is a common mistake. The coil above the surface should be in the same plane, that is, there is no need to lift it at the end of each movement.
- Having discovered an object , you need to get close to it from several sides, understand where the signal from the metal disappears, and dig in the area where the object is supposed to be located.
Sensitivity
This characteristic directly affects the detection depth of the metal detector. It is no secret that searching for ancient coins at great depths requires a high level of sensitivity of the metal detector. But increasing sensitivity will not always improve search results. For example, near power lines, a metal detector with sensitivity turned up to maximum will literally begin to react to the air. Or when searching in a heavily littered area, a high level of sensitivity is also not required. A metal detector with sensitivity set to maximum will also operate unstably on highly mineralized soils.

Kinds
Metal detectors are divided into several types. Some of them have an outdated design and are not produced, although they are still used and sold.
By the nature of the action
Based on the nature of the action, devices can be divided into:
- dynamic;
- static.
Electronics

- analog;
- microprocessor.
By technology
The following types of metal detectors can be distinguished, used to search for non-ferrous metals.
- BFO. Developed a long time ago. Leading manufacturers not released, but is still used by search engines and can be purchased inexpensively. In the simplest models there is only an audible warning, while others also have a visual indication. The device compares the reference radiation and the frequency of the LC generator, thanks to which it determines whether the metal is ferrous or non-ferrous. At low cost, it has a number of negative characteristics:
- small working depth,
- job instability
- poor sensitivity and low recoil on wet and mineralized ground.
- TR. Also refers to early types of metal detectors. Determination of metal occurs according to the principle induction balance. Distinguishes between metal types and is capable of working at great depths. Functions poorly or even does not work at all on:
- littered
and highly mineralized soil.
- VLF. The most common, as it has great functionality. Unmistakably able to distinguish ferrous metals from non-ferrous ones, as well as non-ferrous metals from each other. Uses:
- very low radiation frequencies,
principle of induction balance.
- VLF/TR. Combines the two technologies and operating principles described above. Sensitivity is high. The larger the coil, the deeper the device can “see.” The settings can be adjusted to filter out:
- interference from garbage,
- background from the ground.
- P.I. The principle of induction balance is combined with the operation of a pulsating electromagnetic field. The most sensitive type of metal detectors. Characterized by the fact that without problems and errors it distinguishes the answer from:
- highly mineralized soil,
salty environment.
- RF. Uses high frequencies for operation. It is used if you want to find something large and located quite deep. Depending on the type of soil, the device is able to find metal at depth up to nine meters. Most often used by search engines whose area of interest includes:
- hiding places,
- large pieces of non-ferrous metal,
- treasures and similar expensive things.
Rarely used as an independent technology for metal detectors. Often combined with VLF technology.
Ground influence filters are easy to install.
On the other hand, problems with discrimination often arise, that is, the device does not always recognize ferrous and non-ferrous metals. It is usually purchased either for searching at the bottom of the sea, or if the type of metal is not particularly important.
Requirements for a metal detector for effective gold search
Typically, a metal detector for gold should be able to do the following things:
- Qualitatively share goals. That is, to distinguish gold, which has far from the best conductivity among metals, from iron. On devices with vDI from 0 to 99, gold often has a vDI in the region of 40-45, and ferrous metal - in the region of 30. The more ferrous metal is affected by rust, the more “colored” the signal it gives.
- The size of the object of discrimination. A metal detector for gold must “catch” the smallest grains of metal, that is, there are certain characteristics.
- Depth. The deeper the metal detector goes, the better.
- Detuning from the ground. Gold is often accompanied by other minerals that can provide leads, even false targets. To cut off such alarms, the ground balance is adjusted manually or automatically.

Additional functions
The simplest metal detector will simply beep if you pass its coil over a buried piece of metal. It will give a signal regardless of whether you find:
- old tin can
- rusty iron rod
- or a non-ferrous metal part weighing several kilograms.
To distinguish the non-ferrous metal we need from the black one, the devices are equipped with a discrimination .
This will save time, effort and frustration from the search process. If the search engine is experienced , it can independently adjust the discrimination parameters. For beginners there are already established values.
Also, a good device has a ground balancing
- mineralization,
- humidity,
- soil consistency.

Good metal detectors are equipped with a number of additional functions that are sometimes very useful :
- customized settings for certain types of soil;
- screen backlight;
- volume control.
The following functions are also available:
- Pin-Point mode. Allows the device to operate in static mode, which significantly increases the accuracy of determining the location of a metal object. Also allows you to use the discrimination function more effectively. The place where the metal object was found is called a pin-point. Almost all metal detectors are dynamic, meaning you constantly have to move the coil above the ground to pinpoint the location of an item. Using the pin-point function, you can keep the reel in one place . The signal will depend on the proximity of the object: the closer, the louder. The peak signal will occur when an object made of non-ferrous metal is directly under the metal detector. Since there is no need to move the device, you will more accurately know where the metal is buried. This function has one drawback - the device will not be able to distinguish whether it is ferrous or non-ferrous metal. Therefore, you need to turn it on when you have already figured out the type of metal in general mode.
- Setting sensitivity. Correct installation of this function comes with experience. A high level will help detect an object at greater depth. But at the same time, the device becomes unstable to interference. This function is used based on a specific situation.
- Threshold background. This sound is produced constantly and depends primarily on the soil. It makes it clear that the device is functioning normally. This is useful if your model does not have a display . The hum also changes when switching to a different type of soil, which is also important information for a hunter of scrap and treasure.
- Detuning from electrical interference. Neutralizes false signals created by power lines, repeaters, running car engines and other emitters.
- Tone identification. Useful for models without a display. Alerts with different sounds about different types of metal and object sizes.
- Low battery indicator. A useful feature that will prevent your metal detector from turning off prematurely.
Criteria for choosing a metal detector for gold searching
The requirements are described, the criteria for choosing a metal detector for coins and gold directly follow from the requirements. We will not repeat ourselves, we will simply decipher how to determine whether a metal detector meets a particular requirement or not.
Division and discrimination
We watch the candidate's tests on YouTube. In Russian they usually write “separation test”, and English-speaking users call such a test “nail test” or “board test”. Because they place an ordinary iron nail next to or on top of the coin. And so that objects do not move, they are secured with dielectric fasteners on the board.

And discrimination and filters - read the description. The thinner the discrimination scale is cut into, the more accurately you can cut off unwanted targets, and the fewer extra holes you have to dig.
The size of the object of discrimination
In short, the shorter the wavelength, the smaller the metal detector will respond to objects. And the wavelength is directly dependent on the frequency - the higher the frequency, the shorter the wave.
The minimum frequency for a gold metal detector is 14 KHz. With less frequency, the likelihood of detecting small objects is greatly reduced.

Depth
We read manufacturers' descriptions, tests, articles, watch videos - how this or that device reacts to fine gold. The only question is that many testers do not bother with special MD settings and work “by default”.
Ground Balance
In English this is usually called "ground balance". We read the description, it says everything - either it is not there, or it is manual, or automatic. The best thing you can come up with is when there is an automatic one with the possibility of manual adjustment.

Review of models and prices
The metal detector market is replete with various conventional (not for deep searching) devices. In any store there are many devices in the assortment that differ from each other in different indicators:
- number of available functions ;
- presence of good discrimination ;
- cost.
If your plans do not include searching for ancient coins or gold nuggets, you can buy simpler models . They are enough to detect non-ferrous metal.
The price of a suitable metal detector for non-ferrous metals characterizes it only indirectly. To search for non-ferrous metals, there is no point in purchasing a “completely stuffed” device and paying an exorbitant price for it. The most important thing is the discrimination , which will allow you to configure the device in such a way that it does not react to ferrous metal that we do not need.
If you still need ferrous metal, read the article about searching and digging for ferrous metal with a metal detector.
On the display (if there is one) or with a sound of a certain frequency, the device will inform you about
what metal is in the ground:
- lead;
- silver;
- nickel;
- aluminum;
- iron.
Iron can simply be ignored.
After working with the sensitivity level, you can adjust the device in such a way that you don’t have to dig the ground for the foil from a cigarette pack or beer cap. All of the above functions are also present in budget models, which are recommended to be purchased.
Popular models:

- MINELAB Go-Find 20. An inexpensive model that is perfect for non-ferrous metal mining. Its price is not higher than 12 thousand rubles. Capable of finding large metal objects at a depth of up to 40 cm. There is an indication of battery charge.
- Bounty Hunter Discovery 1100. Good choice for 9-11 thousand rubles. It has slightly less power compared to the previous model. It will not react to very small objects, focusing your attention on large pieces of metal.
- Garret Ace 150. The model is successful, but you will have to hunt a little for it, since it was recently discontinued. But among private advertisements, a used device is often found. A new one costs about 12,500 rubles. Excellent for non-ferrous metals. Finds even small objects at a depth of up to 30 cm, and is able to find large ones even deeper. One of the shortcomings is that there is no battery charge indicator.
- Garrett Ace 250. According to many search engines, this is the best solution for beginners. The device has five search modes, so you can set the settings automatically and accurately. The detection depth is greater than that of previous search models - up to 60 cm. Relatively lightweight - 1.2 kg. But the price is a little higher - it will cost an average of 23,000 rubles.
- Minelab X-Terra 705. If the most important thing for you is the search result, and not the cheapness, one of the best professional metal detectors for searching non-ferrous metals is this model. It has four modes that are configured by the operator, + “all metals” and “iron masking” modes. It has an advanced pin-point designator, which not only accurately indicates the location, but is also able to determine the size of the object. Searches at a depth of up to 80 cm. It has a number of functions that significantly simplify searches on difficult soils. The device costs about 33,000-38,000 rubles.
All the described models have several search modes and can react both to all metals and only to non-ferrous ones, which is what we need.
The best professional metal detectors
The classification of metal detectors into the professional segment is due not only to the price of the device. Professional metal detectors require a more thoughtful approach and more extensive experience from the operator than amateur ones.
As Goblin says, “there is an opinion, and not only mine,” that a professional differs from an amateur in that he receives money from a customer or employer for his work. And the amateur does the same thing, but “for fun.” Hence the paradoxical conclusion: even the cheapest metal detector can be said to be professional. If he solves the problems of a professional.
Here is a rating of devices usually positioned as professional.
Fisher Gemini 3
The unique deep MD is built according to the RF scheme - this explains the absence of frames and the presence of two “suitcase doors” - the receiving and transmitting antennas. A truly professional device designed for deep search of large masses of metal - this is the reason for the choice of the Gemini 3 metal detector, for example, by housing and communal services workers. They use it, for example, to trace “lost” pipelines. You can assemble a “dumbbell” from a “suitcase” and walk with it, or you can take a partner and carry the antennas separately. There are no wires between them.

Gemini 3 operates at a frequency of 81.9 kHz, but these are not quite the same kilohertz as VLF. Therefore, the detection depth of massive objects such as a car reaches six meters.
The scope of application of this device is very wide, but has little overlap with the usual search for coin coins, horse meat, scales and the like for amateurs. It can be useful when digging in the old days and during the war, but there are also more convenient depth diggers.
Minelab GPZ 7000
What distinguishes a professional from an amateur is also the choice of the range of use of the tool. A pro will use a device for a specific task, while an amateur will prefer a universal one. From this point of view, the Minelab GPZ 7000 is truly a professional metal detector. 700,000 Russian rubles - not every amateur can afford to spend that amount on a hobby. But an Australian professional gold miner can.

GPZ 7000 allows you to pick up grains of gold weighing less than one gram from depths at which universal metal detectors detect only ferrous metal. And it’s no smaller than a soldier’s helmet.
Note that the golden minelab weighs a record 3.2 kg and therefore comes complete with unloading - try swinging a Mosin rifle for a day.
Fisher F75
“The Guard dies, but does not surrender” - the words of General Cambronne can also be attributed to the honored veteran of instrument search. This universal MD returns every ruble invested in full. Let's make a reservation: in capable hands. It’s hard to classify it as “plug and play.”
It is better, of course, to take the Fisher F75 of the second generation, with a black bar - Black Edition. Its search conditions are 15–20% better than the same 75, but with a golden rod. Frequency 13 kHz, ground balance manually or automatically, using the FastGrab function.
Among the features, we note the very conveniently adjustable FeTone - the volume of ferrous metal. When the iron still sounds, but quietly.

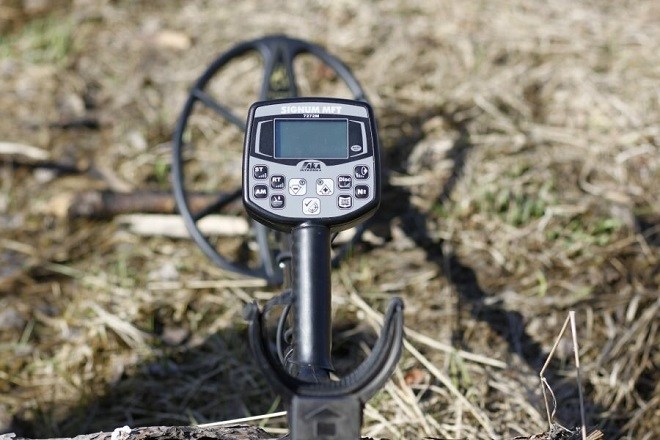
AKA Signum MFT 7272m
The domestic fighter in the cohort of honored foreign veterans feels quite good. Its search conditions and service functions - for example, indication of the nature of the target not only using VDI, but also with a hodograph - determine such a high place. The Russian MD seems to have inspired the creators of the Polish Rutus Alter 71, an outstanding Polish metal detector that was not included in the rating only due to its low prevalence. Signum can operate at frequencies from 1 to 30 kHz - determined by the coil used. There are both single-frequency and three-frequency coils of different sizes on sale.

XP Deus
The object of desire, envy, love or interest of users and manufacturers of metal detectors around the world. XP Deus is a super lightweight device with its own built-in batteries and no wires at all. It’s not for nothing that Deus is translated from Latin as “god.”
Deus carry a recognition unit directly in the coil. Therefore, when buying a new coil, a treasure hunter is purchasing a new metal detector. The control unit contains the actual control and indication. The same functions are duplicated by Deus WS4 or WS5 headphones. In principle, the metal detector works quietly even without a block - a coil, a rod and headphones. Or a reel, a block and a rod.
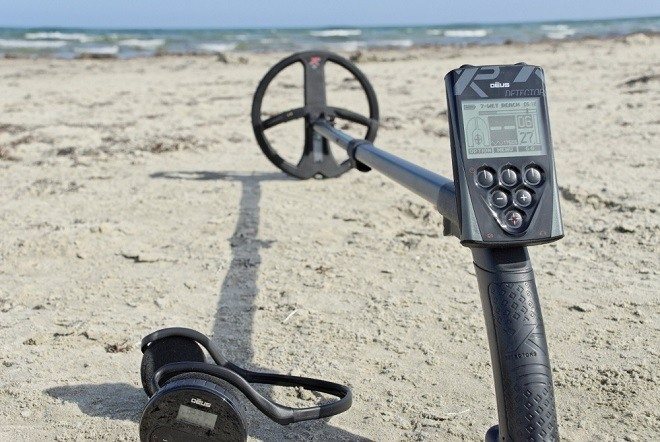

All modern Deus coils allow you to work at several - up to 5 different - frequencies with the possibility of shifting to detune from EMF.
Undoubtedly, Deus is the most technically advanced and beautifully made device costing $1000 give or take a hundred.
Read also: Metal detector for underwater searching: how to choose and which one is better!
Accessories
There are a lot of useful additions to the metal detector that you can purchase right away:
- Additional batteries. It won't be good if you just get the hang of it and start finding something, but the battery immediately runs out and you don't have a spare one.
- Protective cover for the control module. Since the work will be carried out outdoors, on the ground or sand, the control unit must be protected from dust and moisture.
- Headphones. They can be either wired or not. And metal objects will be heard better, and the battery will not drain so quickly.
- Additional reels. With their help, you can better choose the option of equipping a metal detector for a specific situation. True, they cost money.
- Display backlight. A trifle, the presence of which will be very useful at other times. Firstly, you can work at dusk and even at night, which is especially important in the winter season. Secondly, such illumination will help well in some situations, for example, in a forest in cloudy weather.
- GPS module. A GPS satellite navigation device can be built into a metal detector. The scope is wide, you can:
- see your geographical coordinates,
record search routes,
- record locations of finds.
You can even carry out full-fledged navigation activities and plot your route “from point to point.”
Don't forget to take a spatula with you, too .
Digital object identification
A useful thing in a metal detector that helps you identify a find without digging it up. Together with the audio response, it makes it clear the approximate metal and shape of the signal source. This function displays the electrical conductivity index of an object detected in the ground. Different metal detector manufacturers use their own conductivity scales. In Garrett devices there is one, in Minelab there is another. Moreover, on metal detectors of the X-Terra series, the VDI numbers differ from the same numbers on the Equinox. But on all devices the principle is the same - the higher the number, the more interesting the find can be. For example, silver rubles, nickels of Catherine II and other large coins sound great and show high electrical conductivity indices. But small Soviet coins, especially those made of copper-nickel, give a low electrical conductivity number.

How to make it yourself
If you have minimal skills in the field of radio electronics , you know how to solder and understand circuits, then making a basic metal detector will not be difficult. Moreover, there are many schemes on how to do this correctly.
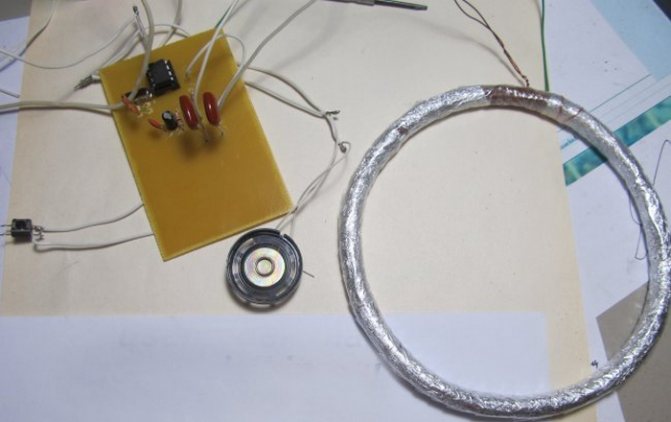

Tools needed to create the device at home:
- Soldering iron and soldering accessories - rosin, tin, and so on.
- Screwdrivers, wire cutters, pliers of various sizes.
- Materials needed to create a printed circuit board.
Radio amateurs use the K561LA7 . Such a device will be able to distinguish non-ferrous metal from black, which is what we actually need. The coil should have 90 turns with a diameter of 230 mm.
You can make different yourself : from highly sensitive models that operate at a distance of up to 20-30 cm , to miniature ones that will show you the location of wiring or other non-ferrous metal objects at a distance of several centimeters.
Detailed descriptions and diagrams are posted in full on the website for radio amateurs radiostorage.net.
The main thing is that it is possible and, if you are a radio amateur yourself, it is interesting.
To learn how to choose a metal detector, watch the video: