Heavy metals in water
Natural fresh waters are polluted with heavy metal ions due to anthropogenic human activities. The danger of water pollution with heavy metals lies in the lack of an effective self-purification mechanism. Impurities migrate from one water storage facility to another, settling along the way in the organisms of representatives of aquatic fauna and depositing in plant tissues.
The main sources of water pollution with heavy metals are industrial enterprises, or rather, insufficiently treated wastewater and slag dumps. Harmful substances enter the soil along with sediments filtered through slag. In the case of injection of industrial waste water into mines and pits, there is a significant impact on the quality of groundwater.
Let us remind you that experts do not recommend drilling wells to create a source of drinking water supply in the immediate vicinity of industrial enterprises. Heavy metals dissolved in water migrate with groundwater and end up in aquifers used as water supplies and in surface water bodies.
How to extract gold from water
17.07.2020
Scientists from Russia have invented a method for extracting gold directly from water that accumulates in industrial waste from man-made facilities.
The unique technology has been mastered by domestic geologists. It allows you to extract gold from accompanying rock located in dumps in places where mineral resources are extracted from the subsoil. To do this, a plastic sorption column with a coal base inside is used, immersed in a well at the site of former mining operations. Over the course of a year of operation, one such module accumulates several tens of grams of gold. The operation of the new equipment has already been successfully tested in the Perm region.
A method for recovering gold from mining waste was invented by geologists from Perm State National Research University (Perm State National Research University). The Perm region is replete with places where waste from mining enterprises has already entered the landscape. Many of them have been present here for over 250 years and contain huge amounts of gold and other valuable elements. All this wealth is washed away from below by groundwater, from which it is proposed to extract the precious metal. Very simple - gold straight from the water!
The extraction method involves the use of simple sorption columns consisting of a plastic pipe with perforations for moisture penetration and activated carbon filling for filtration. The cost of manufacturing one such module is no more than 10,000 rubles. While in the well, such a device passes ground moisture through itself and filters out gold particles, accumulating them in the coal core. At the end of the working cycle, the filling is extracted and processed to extract gold and other valuable resources.
The advantage of this technological method lies in the possibility of using many similar installations within the area of one dump. At the same time, the extraction of the required element becomes several times more efficient.
According to Vitaly Bryukhov, head of the laboratory of the Institute of Natural Sciences at Perm University, over the past two and a half centuries of active development of fossil resources, many waste dumps of technogenic origin have remained on Russian territory, suitable for the beneficial use of new technology.
The advantages of the new method of extracting gold precious metal include complete environmental safety, high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
According to the developers, the productivity of each sorption column can potentially reach several tens of grams of gold per year. The volume of production depends on the precious metal content in the dump rocks and in the gold-bearing waters beneath them. The production cost of one such filtering device is within 10,000 rubles. Moreover, the installation is designed for reusable use over several seasons. Only the internal carbon filling must be replaced annually. The technology has already proven itself successfully in trials from 2021 to 2021.
Now university specialists are trying to patent a new method of gold mining. In the near future, it is planned to widely implement the developed technology in all Russian regions where there are man-made accumulations of mining waste. Scientists are also going to increase the power of their modules and turn them into industrial-scale filters for processing associated rocks to obtain valuable resources.
Source: © Russian RT TV channel
More news
- Pope's seal discovered in Britain
- Brasher's gold doubloon is back up for auction
- A Russian was detained for gold smuggling
to news list
Well water is a source of gold
But heavy metals dissolved in water are not always undeniably harmful. For example, in New Zealand, gold and silver are mined from water. In geothermal wells, the walls of which are composed of rocks rich in precious metals, a high concentration of gold and silver ions is observed in the water. If we consider the silver content in water in absolute values, then a liter of water contains two milligrams of silver and one hundred times less gold. If there is an effective technology for extracting precious metals from water, a well with a flow rate of 100 l/min will produce gold worth $2.7 million per year.
Geothermal wells in New Zealand are located in the Tuapo volcanic zone. Research carried out by geological groups has shown that at least 70 kg of gold and about 7.5 tons of silver can be extracted from the water annually. Water heated by the magma dissolves metals and washes them to the surface, precipitating them as sulfur compounds on rocks. One kilogram of soil can contain about 1 mg of gold.
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no reliable and safe technology for extracting gold from water, since substances of a high hazard class - arsenic and antimony sulfides - are used to adsorb dissolved precious metals.
Do you know?..
The geothermal spring in the Tuapo zone in New Zealand has an extremely romantic name - Champagne Pool, which translated into Russian means “Champagne Pool”
In what water can you find gold?
The precious metal can be found in sewer, tap, sea and other types of water. The gold content in water is low. Most minerals are found in ocean waters.

Gold in the water
The bottom of rivers consists of sediments that lie on bedrock, the so-called raft. There are deposits on the raft that are washed away by currents of water. And also streams can wash gold from the mountains. And since it is heavy, it settles to the bottom, where it is retained by stones, sand, clay and other sediments.
The greatest amount of gold forms in deep bodies of water or in places where the flow rate is slow, as well as in places where there are large rocks and boulders. Gold can be found in places where the river flows onto the plain. Metal is also deposited where the river widens and the flow of the reservoir slows down. Previously, along the river one could find nuggets that were thrown out by the flow of water after the erosion of gold-bearing veins.
The precious metal was discovered in sea water at the beginning of the 19th century. But its prey from the water did not spread. Gold particles are found in rock sediments and in beach placers. Minerals enter the water during the destruction of rocks and shores, forming placers. They settle to depths of five to fifty meters over hundreds of kilometers.
No one knows the exact amount of gold in sea water. It is estimated that this is approximately four to ten mg per ton.
Gold enters sewer and drainage water from industrial facilities, electronics factories, dentistry, and jewelry workshops. American scientists, after research, found that sewers contain more gold metal than reservoirs. No one extracts metal from these waters because it is unprofitable. But scientists are looking for a way to purify wastewater and extract the precious metal from it. It is quite possible that such methods will soon be found, and with their help it will be possible to drink environmentally friendly water and enrich countries with valuable metals extracted from wastewater.
In Japan, from the sewerage system of the city of Suwa, it was possible to obtain 2 kg of gold from each ton of ash. Ash formed on sewer filters and retained and accumulated gold minerals thrown out from industrial production.
We climb to the depths
If you are interested in searching specifically from the depths of rivers, lakes and reservoirs, then you will need not an ordinary metal detector, but a special underwater metal detector or a powerful search magnet. And, of course, a boat that allows you to explore the maximum area. In this case, the extraction of scrap metal from water becomes more efficient.
Searching from a boat is simple - the search magnet is tied with a fairly strong (preferably thin, but VERY strong) rope and thrown overboard, after which the person sits on the oars and rows in an arbitrary direction. Any objects from the bottom, be it sunken fittings, a watch, a knife, a bicycle frame or a caterpillar track, cling to the magnet. All you have to do is check your catch from time to time by pulling out the magnet and removing the catch.
Video - searching in boats using a search magnet:
The cost of magnets varies greatly. Some models can be purchased for 800 rubles, while others can cost up to 10 thousand rubles. First of all, it depends on the power. The more expensive the magnet, the more powerful it is. The weakest ones have a clutch capacity of 80-100 kilograms. The grip of the most expensive ones can reach up to 600-800 kilograms. But most search engines prefer to find a compromise by purchasing search magnets with a clutch from 150 to 250 kilograms.

Finding scrap metal with a search magnet
You should be very careful when choosing a clutch. Keep in mind that the number indicated in the characteristics simply demonstrates the power of the magnet, and does not indicate its exact value. After all, if the magnet’s adhesion is 100 kg, then it is able to demonstrate it in perfectly clear water, being close to a large object that is not hidden by a layer of silt. He most likely will not be able to get the same object in muddy water, and even if it is hidden by a layer of sand or silt. Therefore, it is better to take with a reserve.
Search magnets can vary not only in cost, but also in design. Single-sided and double-sided models are available on sale. The first ones have one ring - on top. The second two are on top and on the side. The latter are noticeably more expensive, but they are more convenient to use as a trawl - drag the magnet along with you and be sure that any metal objects capable of magnetism that get in its way will become your prey.
Metal mining methods
Extracting gold from radio components at home can be done in different ways. Each master engaged in such activities has his own secrets for obtaining gold refining.
As preliminary work, many craftsmen first sort the raw materials at their disposal. All parts are divided into two large groups: new and old parts. Soldered products are also transferred to the pile with the old ones. Sorting is then done within these two groups. In each group, elements rich and poor in content are separated from each other. At this stage, the raw material should be freed as much as possible from unnecessary parts that do not contain gold. Why is it important? When we mine gold at home, the question arises of reducing the consumption of reagents and reducing the time for the entire process, therefore, the more unnecessary parts we eliminate, the more we save on costs.
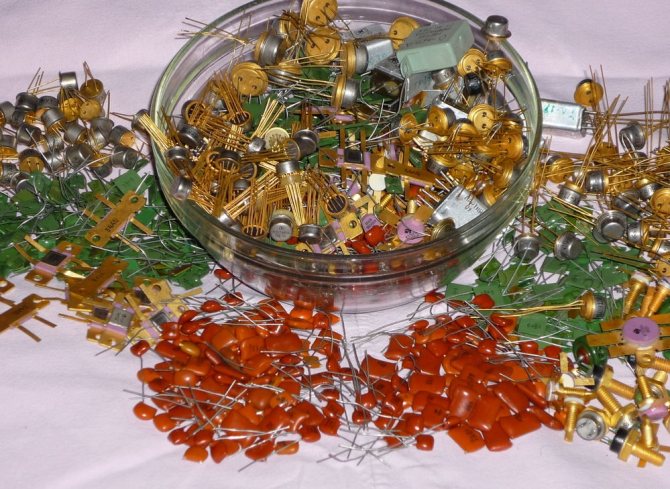

Many also carry out additional processing of the soldered parts, biting off the soldered ends from those parts that did not come into contact with the solder and retained the gold plating. The final sorting is done using a magnet: elements are divided into those that are magnetic and those that are not. As a result, after sorting, you will have several piles of parts, each of which can be processed separately.
Regardless of the type of parts, precious metal refining at home is carried out using the etching method. The basis of the method is the inertness of the noble metal. Gold does not react with other chemical elements; otherwise, nuggets of the metal would not occur in nature. The well-known exception to this rule is the dissolution of gold in “aqua regia,” which is a mixture of two concentrated solutions. Hydrochloric acid is mixed with nitric acid in a ratio of one to three.
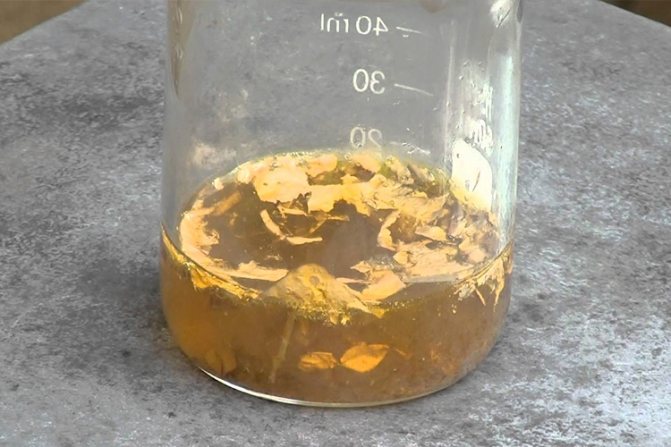

Obtaining gold from radio components at home involves making “aqua regia” yourself. The resulting mixture should be colorless, but over time it changes color to a yellowish tint. “Royal vodka” has an unpleasant, pungent odor characteristic of nitrogen and bleach. The solution must be prepared immediately before use, since over time its oxidizing qualities will decrease.
During the reaction, other components of the parts oxidize and dissolve; gold cannot be oxidized, so it only needs to be precipitated. The procedure can be described in the form of a diagram: we mine gold at home using “aqua regia” - we precipitate the metal, adding a reagent - we filter the solution to separate the gold flakes.
To precipitate the precious metal, one of the following reagents is suitable: hydrazine, oxalic acid, hydrogen peroxide, sodium sulfite or pyrosulfite, ferrous sulfate. It is the latter that is most often used. After all the necessary procedures have been completed, the gold will float in the solution in thin pieces, similar to foil flakes. In order to get them, it is necessary to filter the solution through a thick cloth, which allows you to separate even small particles of metal.
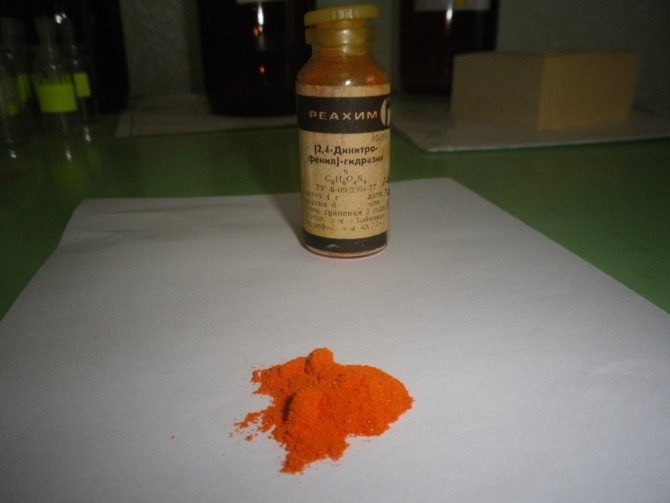

Gold at home must be extracted using high-quality reagents, otherwise you will either fail, or the costs of etching will exceed the final yield of the precious metal. All reagents must be of high quality and not spoiled; the containers for carrying out the reaction must be enameled or aluminum. The efficiency of extracting the gold component from radio components will also depend on the preliminary cleaning of the raw materials from excess parts. Organic components can be removed by calcination, the rest can be removed mechanically. If the devices contain iron, then its remains can be removed using a magnet after all the procedures.

It is also important to remember that when we mine gold at home, we do it for our own benefit, but not to the detriment of our health. You should only work in a special uniform that protects your skin and respiratory tract from exposure to chemical reagents. Poor health will not allow you to feel the joy of the resulting piece of precious metal.
Looking on beaches near the water
Beach searching is quite popular. Some searchers limit themselves to jewelry and coins, but such searches are not always successful, and competition in this area is very high. Finding scrap metal on the beach, on the other hand, may be less lucrative, but is almost always satisfying. To do this, use a metal detector suitable for working in water. They travel with it both along the surf and at shallow depths near the shore.

Finding scrap metal on the beach
Metal objects that fall into the water (especially in lakes and freshwater reservoirs) can lie in the water for many months and even years, but gradually the waves push them closer to the shore. Sand and silt can hide them, so thousands of people can walk by and not notice. But if you have a metal detector at hand, you probably won’t return home without interesting finds.
If we are talking about scrap ferrous metals, then it is worth looking on Soviet beaches, especially those that were near a boat station, fishermen’s parking lot or a concentration of water equipment.
What can you find on the beach
On such beaches (especially at low tide, if we are talking about the sea or a reservoir) you can easily find anchors, old anchor chains, spare parts and body parts of ships.

Old anchor on the beach
Searching for scrap metal on the beach will be complicated by signals from small targets - corks, beer cans, can ears, etc. Therefore, if you are going to look exclusively for black scrap metal, then you should reduce the sensitivity of the device and turn off the colored signals.
On some remote and inaccessible beaches you can even find a long-forgotten car. Also a good find, plus 500-600 kilograms of ferrous metal to your loot.

Rusty car on the beach
Use a magnet on the bridge
Some people, without a boat, prefer to use magnets on bridges, crossings and piers. This is also an interesting solution. It is enough to stock up on a long rope, throw the magnet off the bridge and drag it several tens of meters along the bottom. After all, people on a bridge can drop a variety of things into the water. And if this bridge has stood in one place for several decades (and maybe even replaced several other, old ones that stood here for a century or two), then the number of finds will increase significantly. Of course, when searching, you should exercise extreme caution so as not to jeopardize your life or health. But still, this is quite an exciting activity that will definitely captivate you.
Video - searching for scrap metal in the center of Moscow from the bridge:
Video - searching for metal with a search magnet at the crossing:
Gold content in sea water and methods of its extraction
According to geochemists, one liter of sea water contains 0.000004 milligrams of dissolved gold, one cubic kilometer contains 0.004 tons, and the entire volume of the World Ocean contains more than 6 million tons.
Gold can be extracted by filtering seawater through adsorbents (fine coal, cellulose compounds, pyrite, sulfide ores, rags soaked in reagents) and then burning or dissolving them.
In addition, the following methods are recommended:
- precipitation by chemical methods;
- electrolysis;
- sorption by ion exchange resins;
- placed in a special container;
- ion flotation through special networks;
- soaked in reagents.
Associated extraction of gold from sea placers
Of practical interest is the associated extraction of gold from titanium-zirconium coastal marine placers. The value and economic significance of coastal placers are determined not only by large reserves of ore minerals, but also by the possibility of complex use of raw materials.
A study of seven samples of sand from titanomagnetite sea placers in Primorye revealed an increased gold content. In addition to the main components (ilmenite, magnetite, rutile and zircon), garnet, staurolite, kyanite, kyanite, sillimanite, etc. can be extracted. The content of ilmenite in various deposits ranges from 0.6 to 19%, titanomagnetite from 1 to 28%.

The bulk of gold (95%) is concentrated in the -0.3 + + 0.1 mm class. No associated gold was found. Gold is mostly thin-plate, scaly, isometric in plan, oval, elongated, less often - irregular in shape, completely rounded, heavily abraded, deeply altered by corrosion processes. Laboratory experiments have established that gold can be extracted using jigging machines, although the mass of one piece of gold (scale) from a sea placer is five times less than the mass of gold of the same size from a river placer. Gold recovery by jigging was 84% from river placers and 67% from sea placers. When cleaning the tailings, gold recovery increases to 88%.
When studying the sands of one of the titanium-zirconium deposits of marine origin in the central region of Russia, it was found that free gold contained 29%, associated with other minerals - 71%. The mineralogical analysis established that the gold is very fine and dusty, the grain size ranges from 0.05 to 0.25 mm (the predominant size is -0.12 + 0.05 mm). The shape of gold grains is lumpy-angular and lamellar. The gold is mostly yellow with only a small amount of greenish-yellow. The surface of most large gold grains is altered by corrosion, some of them are covered with a thin film of iron hydroxides, and some grains are rounded. The purity of gold, as determined by the largest slightly corroded crystal, is about 890.
The processing of titanium-zirconium sands in semi-industrial conditions was carried out according to a scheme including screening, disintegration, mechanical scrubbing, desliming and flotation. Selection of collective flotation concentrate and finishing of final concentrates was carried out by a combination of magnetic and electrical separations with flotation and gravity processes on a concentration table. The highest concentration of gold was observed in rutile concentrate and middling products from the electro-separation of non-magnetic and magnetic fractions.
A noticeable concentration of gold is also observed in zircon concentrate. However, the extraction of gold in these products is low, and the bulk of it is lost in quartz sands, according to the portal fishingby.com. The recovery of gold into the collective flotation concentrate is 22% of the original or 75% of the gold found in the sands in free form.