What is red gold
This is not a pure metal (gold without impurities, 999 fine - yellow, without redness), but an alloy of gold and copper. It is copper that gives it its exquisite reddish tint. The technical term “red gold” has long been outdated and is used only colloquially.
Such an alloy is now very rare and is practically not used, since it is very impractical and inconvenient for everyday use. Jewelry made from such gold can only be obtained by individual order from a jeweler or antique dealer.
The cost of red gold
In order to answer the question of how much red gold costs, you need to establish what standard we are talking about, since this is a fairly broad term. Red gold cannot have a purity of less than 916. Depending on the purity, the price can reach up to 2.5 thousand rubles per 1 g, while the cost of a product made from 585 purity is about 1.6 thousand rubles per 1 g.
To find out the exact price, you need to know the exact sample of the alloy. Currently, this term refers to alloys having a purity of 916, 958, 980 and 999. This means that an ingot weighing exactly 1 kg contains, for example, 916 grams of gold, the rest is alloy (copper, silver, nickel). Accordingly, if an ingot weighs 1 kg, it contains 999 g of gold and only 1 g of additives - this is the highest standard at the moment.
The table below will help you find out how much red gold will cost: the price of its various samples is given in it. It should be noted that these prices are approximate and are given for general information, as precious metals change value in international trading, like oil and other assets.
Prices are as of December 1, 2021.
| Try | Price for 1 g, rub. |
| 916 | 2200 |
| 958 | 2300 |
| 980 | 2400 |
| 999 | 2500 |
It should be noted that the price depends not only on the gold rate currently set by the world gold and foreign exchange fund, but also on the form in which it may be. Bank bars and hallmarked ounces are sold by banks at the same price. Pawnshops accept scrap gold at a different, usually lower, price. Jewelry is assessed not only by the amount of precious metal, but also by the quality of work, by the content of precious stones or inserts from other metals, etc. Accordingly, their retail value may also differ. At the same time, gold in the quotations of precious metals on the world exchange cannot be lower than silver and higher than platinum and palladium.
History of origin
Chervonny (scarlet), translated from Old Church Slavonic, means red, scarlet. In Tsarist Russia, chervonets were originally the name given to foreign gold coins - ducats, sequins, florins. Own coins have been minted in Rus' since the 15th century as award insignia.

The first Russian chervonets as a means of payment appeared as a result of the monetary reform carried out by Peter the Great. In terms of weight and alloy value, they corresponded to foreign coins and were intended only for settlements with foreign subjects.
A common practice was to make expensive jewelry from chervonets, because purer gold simply did not exist at that time due to the impossibility of higher purification. Therefore, red gold is still mistakenly considered to be the name of a chemically pure element.
Little Russia and Great Russia
Little Russia (Little Rus') is a name that appeared at the beginning of the 14th century. After the Tatar-Mongol enslavement of Russian lands, only two regions remained free in Rus': Galicia-Volyn and Vladimir-Suzdal, which actively maintained relations with the Patriarchate of Constantinople. After the Kiev Metropolitan left his residence in 1300, the Galician princes began to seek the creation of their own separate metropolis. In 1305, the Galician metropolis was created, independent of the Kyiv metropolis. In order to distinguish one Rus' from another, the practice was established in Constantinople to call the ceded part of the territory of the Galician-Volyn lands - Little Russia, or Little Russia.
The concepts of Little and Great Rus' came into official use in 1361: when two metropolises were formed - one in Great Rus' with its center in Vladimir and Kyiv, and the second in Little Rus' with its center in Novgorod and Galicia.
“Little Rus'” included 6 dioceses of the Galicia-Volyn principality. The remaining 12 dioceses, including Kyiv, began to be called Great Russia. Based on the name of the territory “Malaya Rus” (“Little Russia”), local residents began to be called Little Russians.
Article on the topic
Rus' is unreal. Six countries that almost became our territories
How it is made
Red gold is obtained by introducing a certain amount of copper into the composition. Such additions to precious metals are called alloys.
Nowadays, an alloy of a similar shade is also used, but its standard is much lower, and in addition to copper, it contains silver. This three-component alloy is widely used today due to its good strength and malleability. It lends itself well to soldering. Products made from this alloy are more durable, and the visual difference between the two types of gold is a slight difference in shades of red and is noticeable only upon close inspection.
Next, watch an interesting video about how gold is made:
Stereotype No. 4. Easier than steamed oil
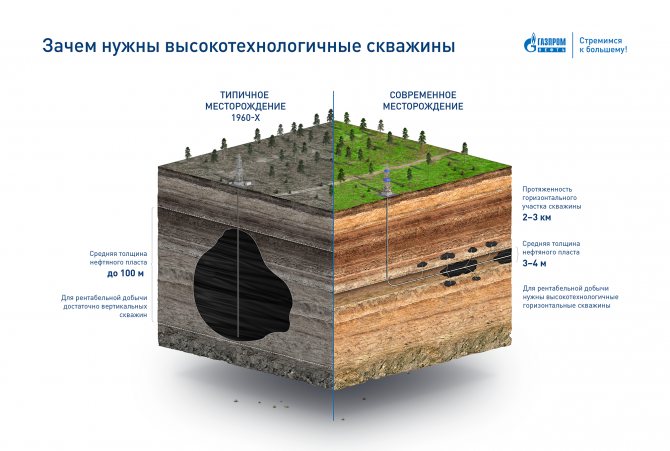
Traditionally it is believed that oil production is a simple task. In fact, as we saw in the previous stereotype, this is not the case. And reducing the permeability of rocks by a thousand times is not the only difficulty. The very shape of the developed strata is also changing. If earlier they were wide and uniform, now they are thin and scattered. Given the scale, drilling today is more like a vessel operation - you need to very accurately drill a well through a thin oil reservoir without going beyond its boundaries. The evolution of well designs shows how the work of oil workers has changed.
Back in the 19th century, oil was extracted in Kuban in special oil wells. Oil was drawn from them using ladles, buckets and tubs. But already in 1866, technologies appeared in Russia that made it possible to machine-drill a well 37.6 meters deep, which produced the first oil gusher in the history of the country.
Then the oil industry developed very quickly: the method of percussion drilling, new methods of strengthening the walls of wells, and reliable welded pipes appeared. All this significantly affected the growth of oil production, its efficiency and safety.
At the beginning of the 20th century, rotary drilling technologies began to be used, which, together with other improvements, made it possible to build vertical wells similar to modern ones. They are relatively easy to build - gravity helps the drilling equipment move downwards, and strengthening the walls of the well is not difficult. And already in the middle of the 20th century, oil workers had all the necessary technologies to develop the giant fields of Western Siberia.
Vertical wells developed homogeneous formations up to 100 meters thick, which lay at a relatively shallow depth. The oil literally came to the surface under pressure in the reservoir.
Over the past 50 years, not only the permeability of oil rocks has changed dramatically, but also their thickness, which has decreased by more than 10 times. Today oil workers have to work with layers 2-3 meters thick.
For such thin and scattered reserves, vertical wells are not suitable - they will have too small a contact area with the formation, which means they will produce very little oil and will not recoup the costs of their construction.
©Scientific and Technical
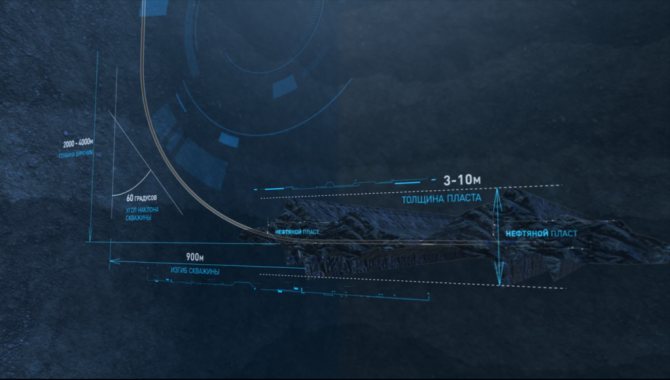
Therefore, today high-tech horizontal wells are used to extract oil. Thanks to special equipment, the shafts of such wells gradually gain an angle of inclination and can eventually bend by 90° in relation to their vertical part.
©Scientific and Technical
Drilling horizontal wells is very difficult. You need to blindly, focusing only on calculations and instrument readings, at a depth of 2-3 kilometers, get into an oil reservoir only a few meters wide. Moreover, then it is necessary to drill hundreds of meters into this formation in a horizontal plane with pinpoint accuracy, repeating its trajectory and not going beyond its limits. Only in this case will the production of such a well be profitable.
©Scientific and Technical
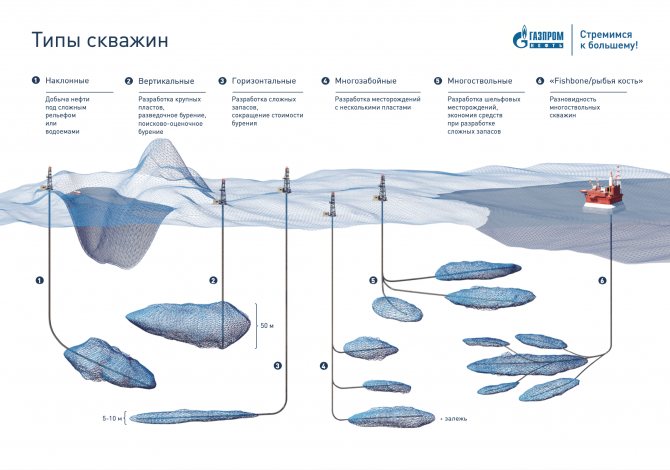
These days, horizontal wells and their variations are the norm. For example, about 80% of all wells that Gazprom Neft drills annually at its assets fall into this category.
Want to know what a well looks like underground? You can see this in a special video.

Drilling control center "GeoNavigator" / ©Scientific and Technical
What other technologies are used by oil workers today? How do they create a controlled crack at a depth of 3 kilometers? Watch this video!
The influence of impurities on the color of gold
Precious metal shades are not limited to red. By changing the composition of the ligature and the proportions of the components, you can achieve the most unexpected colors:
- red – 33.5% copper and 8% silver;
- pink – 9% silver and 32% copper;
- lemon – 30% silver, 11.5% copper;
- white – 25% nickel, 10% silver, 3.5% zinc and 3% copper;
- olive – 15% silver, 6% copper and 4% cadmium.
With the development of technology, new chemical compounds appeared - intermetallic compounds, which further expanded the color palette:
- amethyst – 21% aluminum;
- blue – 54% indium;
- black – 25% cobalt.
History of red gold
The above-mentioned alloy was gaining popularity already in the 18th century. It was used to make coins. Much less common in jewelry craft. In pursuit of status and expensive unique jewelry, the elite of that time went to melt down gold chervonets. Initially, all foreign coins made of high-quality alloys were considered chervonets.
Later, Russia began minting its own copper-infused gold coins, which had no face value. One of the names is red ones. At first they were used exclusively when trading with foreigners. Starting from 1716, they were used within the country, and the chervonets appeared with a denomination of 2 rubles. In 1898 – 1911, gold coins in denominations of 5 and 10 rubles appeared.
Today, the term “red gold” is outdated and is used only in everyday life. There are several versions of where this name came from. Some of them are:
- At that time, red worms were actively used. Their use gave the gold a red tint.
- From the word "czerwony" of Polish origin, which literally translates as "red".
- From the word to paint (“to worm” from Old Church Slavonic).
You may be interested in: Gold and silver: which is heavier?
On the territory of Rus' from 1700 to 1900, chervonets (gold coins) were popular.
Compared to the abundance of modern jewelry, only wedding rings and rings were made from gold, which were quite fragile. That's why they were made thick and massive.
In addition to copper, the following are added to the alloy: platinum, nickel, silver, zinc. Such manipulations are carried out to improve characteristics such as: increasing the density of the alloy, giving even greater shine and a variety of shades. Interestingly, for jewelry made of red gold, an alloy of at least 916 standard is used. Increasing the sample, accordingly, increases the weight of the product.
The presence of silver gives such an alloy strength, but at the same time does not affect its ductility. Changes the usual yellow color to light yellow.
An admixture of copper adds strength and reduces resistance to corrosion, coloring the gold red.
An alloy containing at least 8% platinum completely changes its color to white and increases the melting level.
Palladium also changes the color of red gold to white.
The presence of nickel improves the ductility of gold.
In the modern jewelry industry, red gold is rarely found due to its fragility; it can more often be found in bank bars and coins. Due to its high corrosion resistance, it is ideal for the manufacture of electronic parts. Precious metal is used to cover contacts, as it is highly resistant to oxidation without affecting electrical conductivity.
It is also found in the design of decorative objects, domes of churches and weapons.
Investments will always be profitable if you invest in this type of gold, and not in currencies or securities, since its price is not so changeable.
Many countries in Europe, Asia and the USA use the karat system for calculating gold samples. Briefly about this principle of sample determination: divide the entire volume of material into 24 equal parts. The carat is assigned based on the percentage of content in a piece of pure gold. The engraving “14K” indicates that 14 out of 24 is gold.
You may be interested in: What does the mark on gold jewelry mean?
In Russia they use the metric system. Jewelers calculate the percentage of gold in a kilogram of alloy.
There is an opinion that all alloys above 750 purity are considered red gold.
Pre-revolutionary Russia divided the following types of samples:
- 82 - the alloy included 82 shares of gold, 4 copper and 10 silver;
- 82 - the alloy included 82 shares of gold, 10 copper and 4 silver;
- 92 - the alloy included 92 shares of gold, 2 copper and 2 silver;
- 94 - the alloy consisted of 94 shares of gold, 1 copper and 1 silver.
At home, you can conduct a small check on the quality of your gold if in doubt. To do this, heat the gold until red hot and see if it has lost its shine and color. If this happens, then you have low-grade metal in your hands. If it remains the same, then you have a pure red precious metal.
Bank and pawnshop employees can set the price for jewelry.
The cost of pure gold is almost twice as high as the cost of the alloy, say 585. The gold that is in banks is 99.9% precious, the remaining 0.1% is an impurity that is included in the composition. You can buy or sell it in bars of different sizes and weights. It is possible to have your own metal account with interest and make a profit from it.
But this makes sense only if the storage is long-term, say 5-10 years. The only disadvantage of purchasing a gold bar from Russian banks is the tax on its value (VAT), which is about 18%, which makes the purchase more expensive.
Jewelry made from 999 fine precious metal also costs a lot of money, since even the smallest jewelry weighs 10 grams.
You may be interested in: How to find out the gold rate at Sberbank of Russia?
But due to its high plasticity, it is not relevant and is almost impossible to wear. It’s a good idea to use such gold to cover dishes, interior items, icons, temple domes and sculptures.
The price of this gold is determined by several factors, namely:
- investor demand;
- volume of production in a particular state, deficit;
- accumulation of gold and foreign exchange reserves and its distribution in banks;
- shape and weight of bars and coins sold.
You can find out the cost of a gram of gold of the highest standard on exchange websites and brokerage houses. It is worth paying attention to the prices of the London exchanges if you want to buy red gold.
Now, owners of Soviet jewelry made of cheap, low-grade red gold are very disappointed with the prices when they try to sell them. Due to loss of relevance and customer preferences. Today, white gold is gaining popularity. It is much stronger and more flexible, which allows you to give elegant shapes to earrings or rings.
In European countries, such gold is not popular because it is not considered to be of high quality. Designers believe that gold jewelry with a red tint is more suitable for adult women.
What are the hallmarks of red gold?
The precious metal content in red gold changed at different times, but never fell below 900. Until 1927, a spool system for testing alloys was used in Russia. It had, rather, not a percentage, but a quantitative expression. The value of gold in the coin corresponded to its face value: a 10-ruble coin of the 1885 model contained 2 spools - 11.62 grams of pure gold with a weight of 12.9 g.
- The coins of the Peter the Great era were 986 fine.
- Under Catherine, the standard of five-ruble chervonets was lowered to 916.
- Nicholas Imperials - 900 standard.
- Soviet chervonets, issued in the years 22-25 of the 20th century, were stamped with the number 900.
How to decipher a gold standard
If we are talking about the metric system, then the mark on the precious metal displays how many grams of pure substance are in a kilogram of the alloy. So, 585 standard means that 1 kg of alloy contains 585 g, or 58.5% gold.
In the karat assay system, a chemically pure substance has a hallmark of 24 carats. A hallmark of 22 carats corresponds to 916 metric hallmarks, 14 to 585.
In the spool system, the unit of calculation is taken to be a pound, equal to 96 spools.
Conversion tables are used to convert sample values from one system to another.
Sample table
| Metric | Carat | Zolotnikovaya |
| 375 | 9k | 36 |
| 500 | 12k | 48 |
| 585 | 14k | 56 |
| 750 | 18k | 72 |
| 875 | 21k | 84 |
| 916 | 22k | 88 |
| 947 | No | 91 |
| 958 | 23k | 92 |
| 999 | 24k | 96 |
Characteristics of red gold
When making alloys, precious metals are diluted with other precious metals, which are called alloys or alloys. Such manipulations are carried out in order to give the alloys the missing qualities.
The yellow color of red gold is diluted with a soft, reddish tint. This is explained by the small amount of copper impurities in the alloy. But if the jewelry has a pronounced red color, then such gold is not red gold, since the content of the alloy in it exceeds the permissible norm.

When making jewelry from red gold, metal of at least 916 standard is used. If a material with a 999 marker is used as a basis, the weight of the product increases significantly to increase wear resistance. Such jewelry weighs 10 grams without changing.
To increase the density of the alloy, increase shine and give it different shades, in addition to copper, the following are also added to red gold:
- Platinum.
- Nickel.
- Palladium.
- Silver.
- Zinc.
- Cadmium.
Copper impurities increase the strength of the pure alloy without changing its elasticity, but reducing its resistance to corrosion. Silver also imparts hardness, while maintaining ductility and malleability. But at the same time it reduces the melting point of gold. Changes color to yellow with a green tint, white with a yellow tint and pure white.
With small amounts of platinum, yellow gold is very effectively colored white. Already at 8.4% white metal content in the alloy, the yellow color disappears completely. In this case, the melting temperature increases significantly.
Nickel increases the strength of the alloy, changing its color to pale yellow. The plasticity of the metal also sharply increases.
Palladium also easily changes the color of a red alloy to white, but not as intensely as platinum does. The yellow color disappears completely when the alloy contains 10% metal. Compliance in processing is completely preserved.
Additions of zinc reduce the hardness of gold, thereby lowering its melting point.
Significantly reduces the melting point of cadmium gold alloy. But at the same time it retains its plasticity in processing.
The traditional yellow color of the red alloy, with a reddish tint, can easily be changed from pink to green and even black with the help of impurities.
Red gold, due to its softness, lends itself well to processing. But in modern jewelry, it is practically not used, since it is very fragile, and is mostly used as investment bars and bank coins.
High standard gold has excellent resistance to corrosion. Due to this quality, it is widely used in the electronics industry. The contacts are treated with noble metal, which protects them from oxidation without reducing the conductivity of electricity.
In chemical production, this type of gold is used as catalysts. It is used in the automotive industry in the manufacture of electronic parts and catalysts, as well as in the decorative design of architectural objects (domes of cathedrals, mosques).
Regardless of how much pure gold costs at one time or another, its price will always be higher than all other varieties of this metal, due to the high purity of the alloy. Investments in it are more profitable than in foreign currencies or securities.
The cost of high-grade gold
The noble metal served as the basis for the emergence of commodity-money relations and to this day is a stable international currency. Its value is formed as a result of exchange trading and has been steadily growing in price in recent years.
Price per 1 gram
You can find out how much a high-grade pure gold alloy costs right now, online, on our website using the chart.
Similar information on changes in the cost of bank gold per gram is presented in tabular format for the convenience of users.
| Price 999 standard according to the Central Bank | Market value of the sample today | Scrap price | Price in jewelry |
Samples of pure gold
An indicator of the amount of precious metal in the final alloy is called fineness. In modern Russia, the metric measurement system is used, where the sample number of a noble metal is determined by the ratio of its grams per kilogram of alloy. In America and many European countries, the carat system is used to establish the standard of precious metals.
The technical significance of pure gold has been lost due to periodically changing standards. Now it is used only in household circulation, to designate the highest quality metal. At the moment, the markers of this alloy are 916, 958, 986 and 999. There is also an opinion that all gold above 750 can be called red.
In pre-revolutionary Russia, the purity of the red alloy was determined using a spool measurement system. Its indicator denoted the ratio of the shares of precious metal with the shares of alloys in the total 96 parts of the alloy. There were the following types of samples of red metal:
- 82 - the alloy consisted of 82 shares of gold, 4 copper and 10 silver.
- 82 - the alloy consisted of 82 shares of gold, 10 copper and 4 silver.
- 92 - the alloy consisted of 92 shares of gold, 2 copper and 2 silver.
- 94 - the alloy consisted of 94 shares of gold, 1 copper and 1 silver.
If you doubt the sample of the red alloy, you can carry out an easy test at home. To do this, you just need to heat the metal until red hot. If the jewelry loses its color and fades, you have an alloy of low quality. But if the metal only turns slightly red, rest assured, you are holding real red gold in your hands!
The price of red gold per gram today is about 2,000 rubles. A more accurate value of the precious metal can be determined in banks or pawn shops. So we have defined what red gold is. And now the story of its origin.
How to properly care for gold jewelry
Gold products are highly resistant to external factors, but need to be cleaned from household dirt. This is especially true for items for everyday wear.
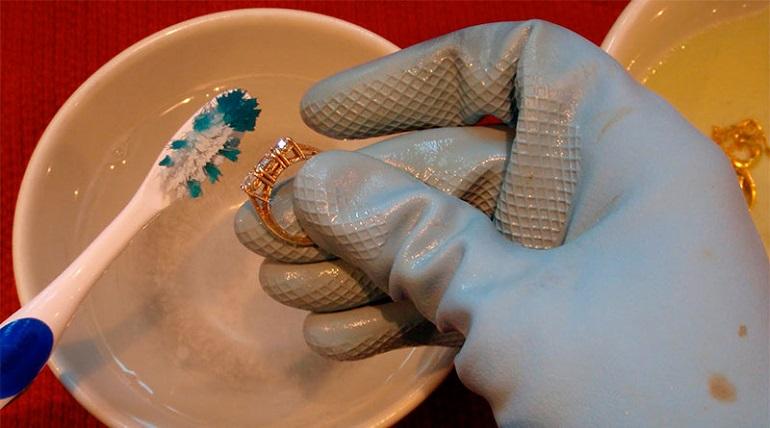

There are several ways to carry out this procedure at home:
- Place items in the saline solution for 12 hours, then rinse thoroughly. To prepare the solution you will need a glass of boiled water and 3 tablespoons of salt.
- You can also use a mixture of ammonia and soap; 2 hours will be enough to clean jewelry, then the solution is washed off with plenty of water. Ingredients: a teaspoon of ammonia and liquid soap per glass of boiled water.
- Without pressing, wipe the products with a cotton swab dipped in three percent hydrogen peroxide, leave for 15 minutes, then rinse with plenty of water.
Plastic or ceramic containers are used for soaking jewelry, but not metal ones. After rinsing, they are carefully and thoroughly wiped with lint-free wipes and polished with suede.
Due to its softness, the cleaning of items and jewelry made of red gold should be entrusted to a jeweler.
How to determine if a product is genuine
The most reliable method for checking the “redness” is considered to be heating, during which the metal becomes slightly reddish. But if you heat a product with a high copper content, it will not only become red, but also dull. But you shouldn’t do this at home on a gas stove or with a candle - it’s better to go to a jewelry workshop, where they will check it using special equipment.
Upon purchase, the consultant must provide a product certificate. Often items made of red gold are sold privately, so to ensure a safe purchase, do not be too lazy to contact jewelers, and if they offer antique pieces, then also to museum experts.
Jewelry made of pure gold (a high-grade alloy with copper) is not intended for daily wear due to its softness, tendency to deformation and abrasion, but this disadvantage can be partially compensated by the massiveness of the ring.