Silver is a beautiful noble metal from which jewelry, coins, home decoration and dishes are made. And although silver items are counterfeited less often than gold items, sometimes it becomes necessary to verify the authenticity of the metal. How to test silver at home, read our article.
Pure silver has a silvery-white metallic hue and is highly reflective. However, if it is not cleaned for a long time, it darkens and becomes dull.
Sample and stamp
In order to check the authenticity of silver, first of all inspect the product for the presence of hallmarks and hallmarks.
The mark may look arbitrary, and sometimes be completely absent from the product. As for fineness, silver items sold on the international market must have a marked hallmark indicating the fineness of the metal. The most common numbers are 800, 830, 875, 925, 960; pure silver – 999 standard.
Do not be upset if you cannot find marks on the product - this does not mean that this is a different metal. Such a product may simply not be certified or produced in a country where the mark is not required.
The numbers on the marking indicate the percentage of silver in the alloy. For example, the 925 stamp indicates that the alloy contains 92.5% silver, and the 900 stamp indicates 90% silver content
There are other ways to test your silver. Let's take a closer look at them.
Leading countries in production
Today, global silver production amounts to more than 20,000 tons per year, most of it in the leading countries:
- Mexico (5900 t/y)
- Peru (about 4,200 t/y)
- China (more than 3400 t/y)
- Australia (1900 t/y)
- Russia (more than 1600 t/y)
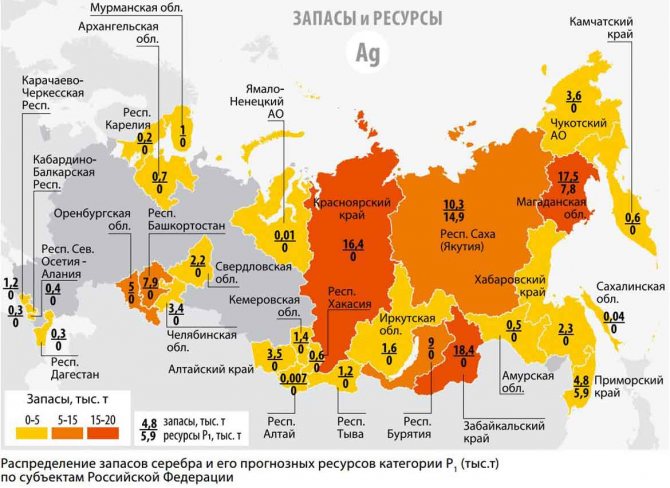
The richest deposits
According to information provided by the US Geological Survey, the largest reserves of silver are: Peru (120 thousand tons), Australia (about 85 thousand tons) and Poland (about 85 thousand tons). The potential of Canada, Germany and Norway is rich in this regard. The Sukhoi Log field in the Irkutsk region is the largest undeveloped reserve in Russia.
Deposits in Russia, compared to the rest of the world, are distinguished by the highest concentration of silver in the ratio of gram of metal per ton of rock.
In the world
Mexico is developing about 200 mines on its territory, the largest of which are in Las Tores (Guanajuato state) and La Encantada (Coahuila state) with deposit volumes of 4.3 and 3.2 million tons of ore, respectively, as well as mines in the states Hidalgo, Zacatecas and Chihuahua with a total production volume of 20% in the country.
In the DPRK, this is the Ying region, which produces 35% of the state's reserves. Next comes Fuwan (Guangdong Province) - this deposit is highly profitable due to the high concentration of silver.
Peru has many small mines, producing 17% of global production. The largest is San Rafael, Eastern Cordillera - about 27% of the country's reserves. Australia - Kirrington, western Queensland. The volume of production at the field is about 43% of the resources of the entire territory.
In Russia
Among the richest deposits operating in the Russian Federation, the following are recognized:
- Lunnoye, Dukat and Goltsovskoye, Magadan region (30% of the country’s production);
- Forecast - Yakutia;
- Ozernoye and Kholodninskoye - Buryatia.
Five large silver mining companies in Russia
- Polymetal Corporation: 800,000 per year, mines of the Khabarovsk Territory and deposits of the Magadan Region, 80% of production.
- Chukotka GGK: Kupol and Dvoinoye fields in Chukotka.
- Millhouse Corporation: Highland Gold Mine.
- .
- .
Magnet
Silver, like gold, is diamagnetic, so you can quickly check its authenticity using a magnet.
Bring a magnet to the item - if it is magnetic, it means that it is either a silver-plated item or made of another metal. If the item is not magnetic, there is a very high chance that it is real silver.
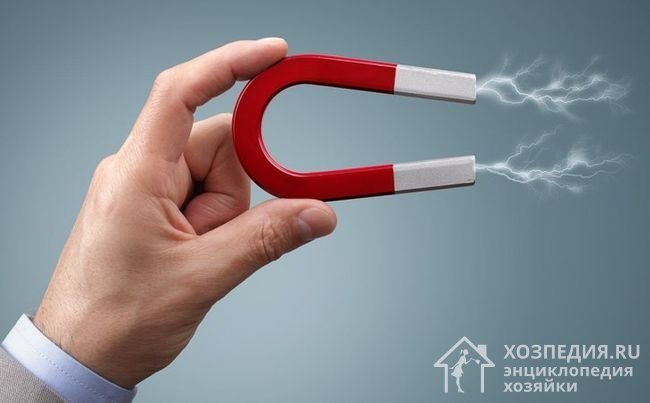

Testing with a magnet may not give the desired result if the main alloy material is copper. So, cupronickel and brass (copper alloys) will not be attracted to a magnet
Areas of application
Each of the physical and chemical properties of silver has found its application in industry and medicine, manufacturing and jewelry.
The ability to withstand heavy loads is used in the manufacture of contact elements in computer technology, electrical engineering and radio electronics.
A special place is occupied by nuclear technology and the defense industry, where silver is used in uranium enrichment.
High thermal and electrical conductivity is in demand in the manufacture of electrical contacts and conductors in precision instruments.
Neutron radiation indicators take advantage of silver's ability to become radioactive.
The ability to reflect is used in the production of mirrors. Photosensitivity is also used by the glasses of “chameleon” glasses and the entire photo and film industry in the production of film.
A colloidal solution of this metal has strong bactericidal properties, which is used by pharmacists in the production of medicines, and by industry in the manufacture of medical devices.
Using silver nitrate, forensic scientists take fingerprints; silver iodide in microscopic quantities causes precipitation. The addition of silver makes the bells and strings sing. And jewelry made from this noble metal can outshine any other!
Thermal conductivity
Silver has the highest thermal conductivity among metals - it heats up quickly and gives off heat just as quickly. Try temperature tests with the product.

If you have a coin or bar in your hands that needs to be checked for authenticity, use ice
Take an ice cube, place it on the product and observe carefully. If the ice melts quickly, as if it were placed on something very warm, you have silver in front of you. This test is suitable for flat items; it does not work well on small jewelry.
You can check a small piece of jewelry by simply picking it up - after a few seconds, the silver item will reach the temperature of your body. If you immerse a silver object in hot water for a moment, it will heat up to the temperature of the liquid in a matter of seconds.

Remember that silver darkens due to high temperature exposure, and in order to return it to its original appearance, you will have to clean the product
Voice test
This test is suitable for checking coins. When tapped, silver makes a ringing sound (especially if it is tapped with another metal). If you already have a proven silver coin, its ringing can be taken as a standard.
Gently tap the silver item (you can use another coin for this): if when you tap you hear a beautiful, open ringing, then this is real silver. If the sound is dull, it means there is little or no silver in the alloy.

A silver service can become a family heirloom and be inherited from generation to generation
lapis pencil
You can buy a lapis pencil at a pharmacy. It is often used for testing precious metals at home.
Wet the product and make a mark on it with a lapis pencil: if the metal changes color, then this is a sign of a fake. Since lapis consists of silver nitrate, it does not react in any way with either silver or gold.
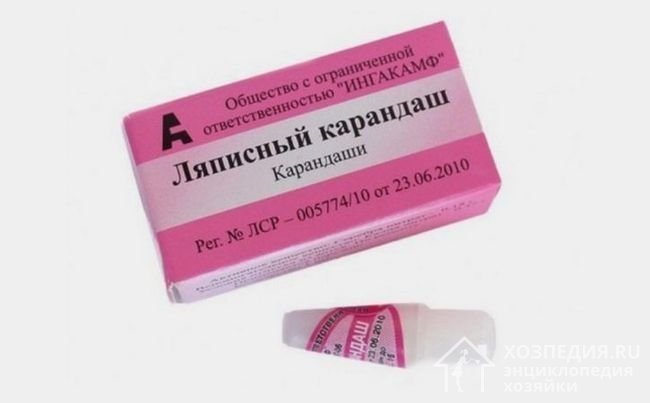
Lapis pencil is a somewhat outdated remedy, and you can’t buy it at every pharmacy.
Where is silver found in nature?
In nature, the noble metal is found as an admixture of gold-silver, copper and lead-zinc ores. In the earth's crust its content can reach 1 gram per ton - this is most often than all precious metals, and in sea water - 0.00004 g/t.
Types of deposits
In general, there are two types of deposits. These are the silver mines themselves. The share of silver is at least half of the total volume of metals mined. The largest of them are located in Mexico.
There are also silver-bearing deposits, where silver is a small part of the total production. The largest deposits of polymetallic ores are located in Australia, Japan and the USA.

Sulfuric ointment
You can check the authenticity of silver at home using sulfur ointment (sold in pharmacies).
Apply the ointment to a small area of the product and wait 2 hours. Remove it from the surface with a dry cloth and carefully inspect the treated area: if the surface has darkened, this is silver; if it has acquired a different shade or remains unchanged, the product is made of a different metal.
The test with sulfur ointment is also carried out in another way: a small area of the product is rubbed with fine-grained sandpaper and lubricated with sulfur ointment. After 15 minutes, the result is assessed. If there is a dark spot left on the treated area, then there is a high probability that this is real silver. Metals such as nickel or stainless steel will not interact with sulfur ointment, and, accordingly, no stains will remain on the product.
To remove dark spots left after sulfur ointment, you can wipe the product with ammonia or put it in a soda solution.
Iodine and chalk
You can test silver with iodine.
In order not to spoil the product, carefully apply a small drop of iodine to the inner surface of the metal - a dark stain will remain on real silver. You can remove traces of iodine after testing in the following way: place the product in a bowl with grated potatoes or sprinkle with starch - under the influence of starch, traces of iodine will change their color and acquire an imperceptible bluish tint, merging with the color of silver.

Chalk not only checks, but also cleans silver. Crushed chalk is mixed with ammonia and the silver items are wiped with a soft cloth.
A similar test can be carried out using ordinary chalk. Rub the silver with a piece of chalk: a dark spot will form on the metal at the point of contact. If the blackness does not appear, you have a fake silver.
You can clean your jewelry using available products. Read how to do this in our article “How to clean silver at home.”
The process of silver formation in nature
On the surface of the earth, metal is formed during the simultaneous decomposition of sulfur, arsenic and antimony ores and their reduction with a variety of organic compounds.
Moreover, it can take any shape with the exception of a solid mass. Thus, intricate thread-like patterns are formed on pieces of coal. But silver is unstable in such conditions; it quickly turns black and, under the influence of temperature and precipitation, transforms into various compounds.

Underground, most minerals are formed from magma. Due to the tightness at the moment of crystallization, they do not have any special beauty. This is how metal ores, which include silver, are formed.
Another thing is hydrothermal vein deposits. These underground voids, formed by hot aqueous solutions and composed of crystals of quartz, carbonate and lead sulfide, become the site for the extraction of silver wire.
How are silver veins found?
An external sign indicating the presence of a silver vein in the rock is a scattering of rust-colored stones on the flat top of the mountain. This is one way to identify a deposit.
Satellites of silver
Invariably accompanying this metal in vein deposits are argentite, calcite, sulfur, arsenic and antimony compounds of nickel, cobalt, etc.
Vinegar
You can test silver with vinegar.
Pour the 9% table bite solution into a bowl and lower the product into the container for a few seconds. Since silver is a low-reactive metal, it will not react with vinegar. If a white coating appears on the product or other changes occur, this is a fake.

You can use a bite to clean silverware and dishes until they shine.
Nitric acid
You can test silver using nitric acid - this test is considered one of the most accurate.
Wear gloves and a protective mask, select an inconspicuous area on the product, lightly scratch it to remove any protective coating, and apply a drop of nitric acid. If you have a low-quality silver alloy - cupronickel or silver-plated brass - a greenish stain will remain on the product. This is due to the fact that the product contains high levels of copper. When exposed to nitric acid, silver will turn dark, while sterling silver (925) will turn creamy.
Today you can purchase a professional silver test in jewelry stores and conduct a chemical experiment at home.
Extraction methods
There are four methods of mining:
- Mine - underground. The deposit is developed using a gallery system.
- Quarry - above ground. Mining is carried out in massive trenches.
- Borehole - excavation of ores to the surface using a drill.
- Marine - work below sea level.
In old times
In ancient mines, rock extraction vaguely resembled a combination of modern mining and open pit methods. The extraction consisted of the following: the rock was heated using fires and then sharply cooled. With the advent of explosives, the appearance of mines began to evolve towards the appearance of modern underground mines.
Modern methods
Currently, silver is mined from deposits mainly underground, using the mine method, open-pit mining is also used, and the borehole mining method is increasingly being used.
Physical impact
You can check the authenticity of silver using physical impact.
Rub the product to be tested in your hands for 1-2 minutes. If you have high-quality silver in front of you, then your hands will remain clean after rubbing; if the product contains zinc impurities, barely noticeable dark spots will remain on your fingers.
Try testing your silver with a needle. If you suspect that you have a silver-plated product, lightly scratch an inconspicuous (internal) area with a needle: a thin layer of silver will easily be removed from a fake, but nothing will happen to the genuine metal.

The expert will give accurate information about the authenticity of silver and determine the content of impurities of other metals
All the methods described above will help determine the authenticity of a silver product with a certain degree of probability. To get a 100% guarantee, have your item examined by professionals: they know exactly how to test silver.
How to extract silver at home
- Method one: the silver-containing element is immersed in a mixture of hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. After dissolving it, zinc dust or shavings are added and allowed to settle until a sediment forms, which is washed with water and dried.
- Method two: a little hydrochloric acid is added to the aqueous electrolyte solution. The part sinks to the bottom until a curd-like sediment appears. The precipitate is left to settle for 24 hours, then the solution is filtered and a little hydrochloric acid is added. The acid is removed, the precipitate is washed with water and dried at 120 °C.
- Method three: to remove a thin layer of silvering, it must be treated with a solution of potassium iodide and metallic iodine preheated to 50 °C.










